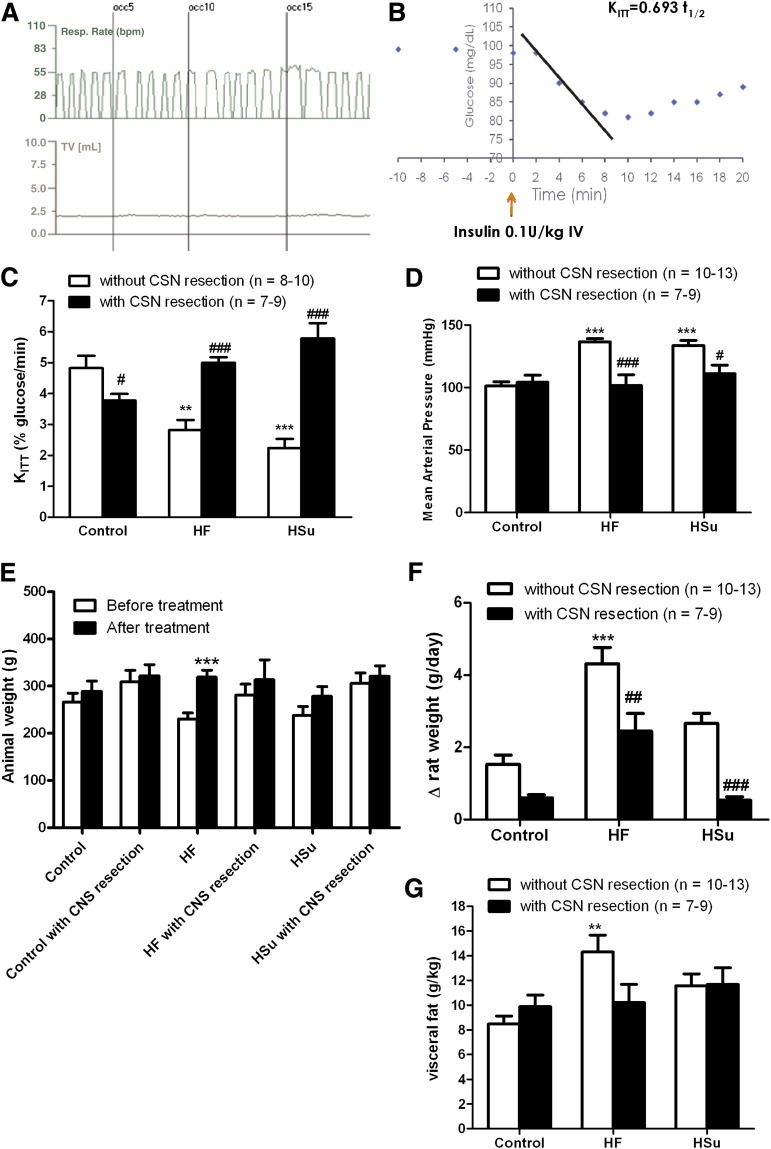
FIG. 2.
CSN bilateral resection prevents IR and HT in HF and HSu animal models. A: Typical recording of respiratory rate (bpm) and tidal volume (mL) in response to ischemic hypoxia, induced by occlusion of common carotid artery in a rat submitted to CSN bilateral resection. The absence of increment in the ventilatory responses confirms CSN resection. B: Representative glucose excursion curve for insulin tolerance test in a control rat. Details on KITT calculation are described in research design and methods. A and C: Effect of CSN resection on insulin sensitivity determined by the insulin tolerance test, expressed as KITT in control, HF, and HSu rats. D: Effect of CSN resection on MAP in control, HF, and HSu rats. E: Absolute weight before and after hypercaloric diet administration and chronic sinus nerve resection. F: Increment in body weight, calculated as total weight variation during the experimental period, in control, HF, and HSu rats with and without CSN resection. G: Visceral fat, weighed postmortem and corrected to body weight in control, HF, and HSu rats with and without CSN resection. Bars represent means ± SEM. One- and two-way ANOVA with Dunnett and Bonferroni multicomparison tests, respectively; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs. control; #P < 0.05; ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 comparing values with and without CSN resection.