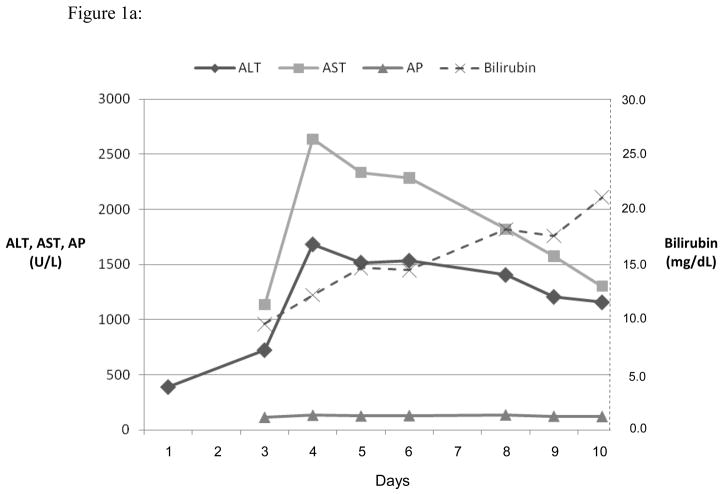
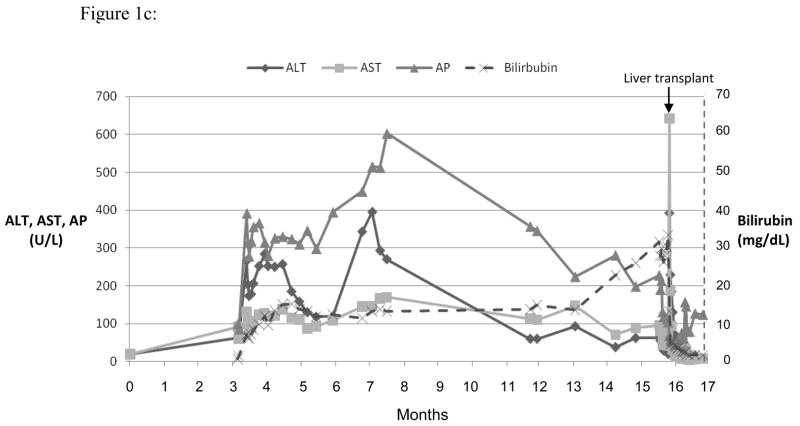
Figure 1.
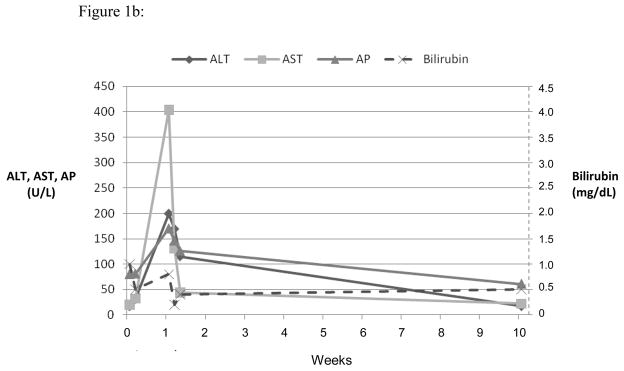
Serum ALT, AST, AP and bilirubin over time after 3 different fluoroquinolone induced liver injuries. Expert opinion causality scores for all three cases were 2, or very likely. (a) Ciprofloxacin induced hepatocellular injury causing acute liver failure and death. (b) Levofloxacin induced mixed hepatocellular-cholestatic injury with recovery. (c) Moxifloxicin induced cholestatic liver injury leading to prolonged cholestasis, ductopenia and liver failure requiring transplant.