Figure 2. Common cellular targets for unrelated tumour virus oncoproteins.
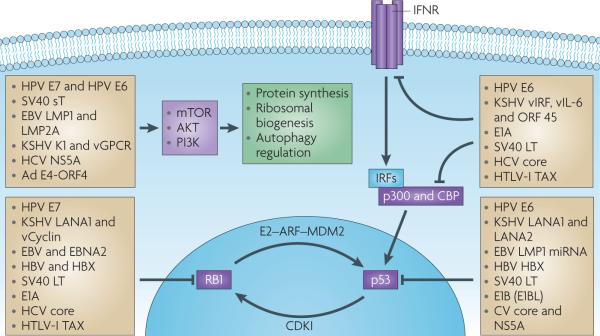
An incomplete but diverse list of animal and human tumour virus proteins that target RB1, p53, interferon and PI3K–mTOR signalling pathways. Most of these viral proteins are evolutionarily distinct from each other and have unique mechanisms for regulating or ablating these signalling pathways. Convergent evolution of tumour viruses to target these (and other cellular signalling pathways (not shown), including interleukin-6 (IL-6)–signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 signalling, telomerase and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signalling pathways) reveals commonalities among the cancer viruses in tumour supressor and oncoprotein targeting. CBP, cAMP-response element binding protein; CDKI, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor; EBV, Epstein–Barr virus; HCV, hepatitis C virus; HPV, human papillomavirus; HTLV, human T-lymphotropic virus; IFNR, interferon receptor; IRF, interferon regulatory factor; KSHV, Kaposi’s sarcoma herpesvirus; LMP, latent membrane protein; miRNA, microRNA.
