Fig. 1.
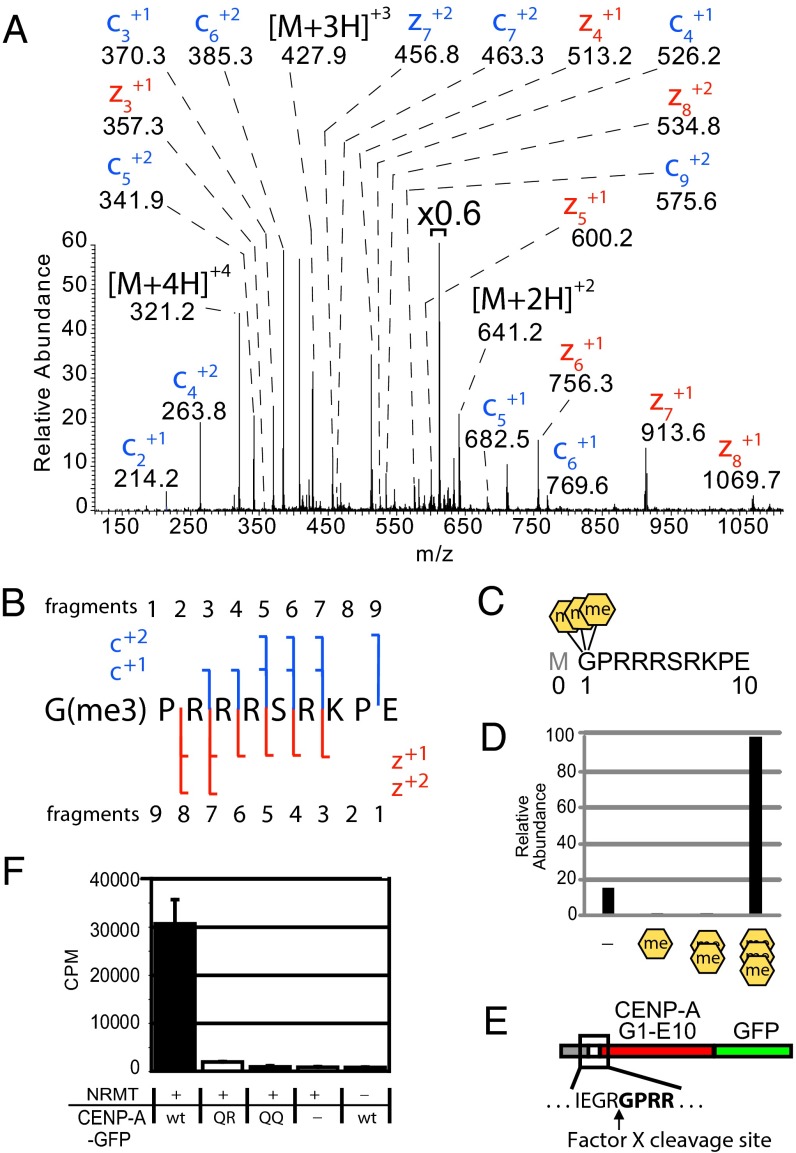
CENP-A is trimethylated on the α-amino position of the N-terminal glycine. (A) CENP-A GluC digestions produced an ETD MS2 spectrum of an N-terminal peptide trimethylated on the α-N position of glycine 1. Value above bracket indicates magnification. (B) Sequence coverage of α-N trimethylated CENP-A ETD MS2 spectrum. (C) GluC cleavages at E10 to produce an N-terminal peptide that had been subjected to proteolytic initiating methionine removal in vivo. A conventional histone nomenclature is adopted for CENP-A where the initiator methionine is “Met0.” (D) Integrated chromatographic peak areas of CENP-A G1–E10 methylated forms. Orange hexagons, α-N methylation. (E) A fusion protein containing amino acids 1–10 of CENP-A was engineered to reveal Gly1 by Factor X cleavage to produce a substrate for NRMT modification. (F) CENP-A fusion protein was methylated using recombinant NRMT and 3H-SAM. Wild-type CENP-A N termini (GPRR-) and mutants in which R3 and R4 were replaced by glutamine (GPQR- or GPQQ-) were tested. P < 0.01, Student’s t test, n = 3 independent experiments ± SD.