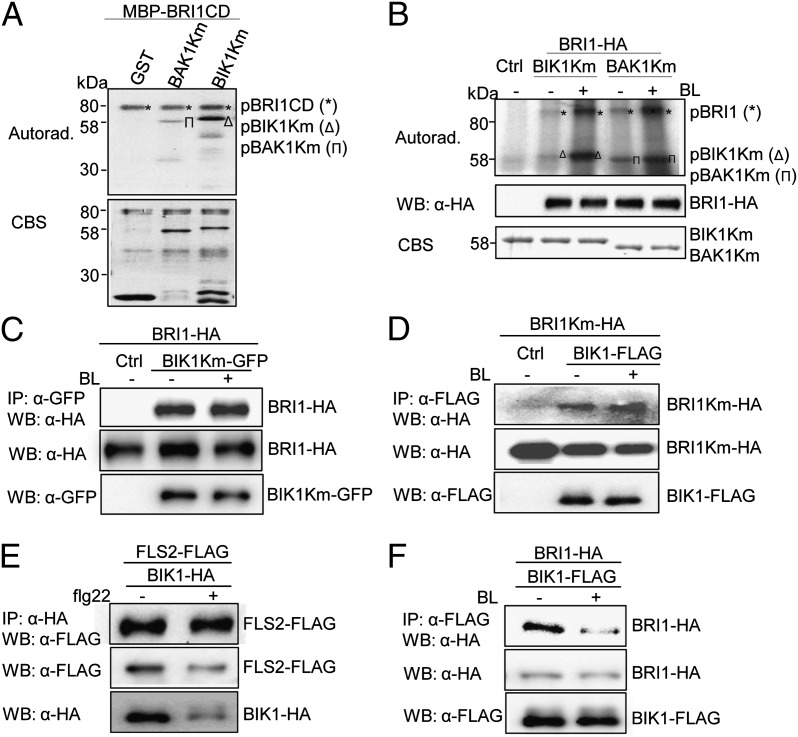
Fig. 4.
BL-induced BIK1 phosphorylation by BRI1. (A) BRI1 phosphorylates BIK1 in vitro. An in vitro kinase assay was performed by incubating MBP-BRI1CD with GST, GST-BIK1Km, or GST-BAK1Km proteins. Proteins were separated by 10% SDS/PAGE and analyzed by autoradiography (Upper), and the protein loading control was shown by CBS (Lower). (B) BL treatment enhances BRI1 phosphorylation on BIK1. BRI1-HA was expressed in WT protoplasts for 10 h followed by 2 μM BL treatment for 2 h. BRI1-HA proteins were immunoprecipitated with α-HA antibody and subjected to an in vitro kinase assay with GST-BIK1Km or GST-BAK1Km proteins as substrates (Top). Middle shows the BRI1-HA expression, and Bottom shows GST-BIK1Km and GST-BAK1Km proteins. (C) BIK1Km-BRI1 association in protoplasts. Protoplasts were treated with 2 μM BL for 2 h. (D) BIK1-BRI1Km association in protoplasts. (E) BAK1 is required for flg22-induced BIK1-FLS2 dissociation. The BIK1–FLS2 interaction was performed with bak1-4 protoplasts. Protoplasts were treated with 1 μM flg22 for 15 min. (F) BAK1 is not required for BL-induced BIK1-BRI1 dissociation. The BIK1–BRI1 interaction was performed with bak1-4 protoplasts. Protoplasts were treated with 2 μM BL for 2 h. The above experiments were repeated three times with similar results.