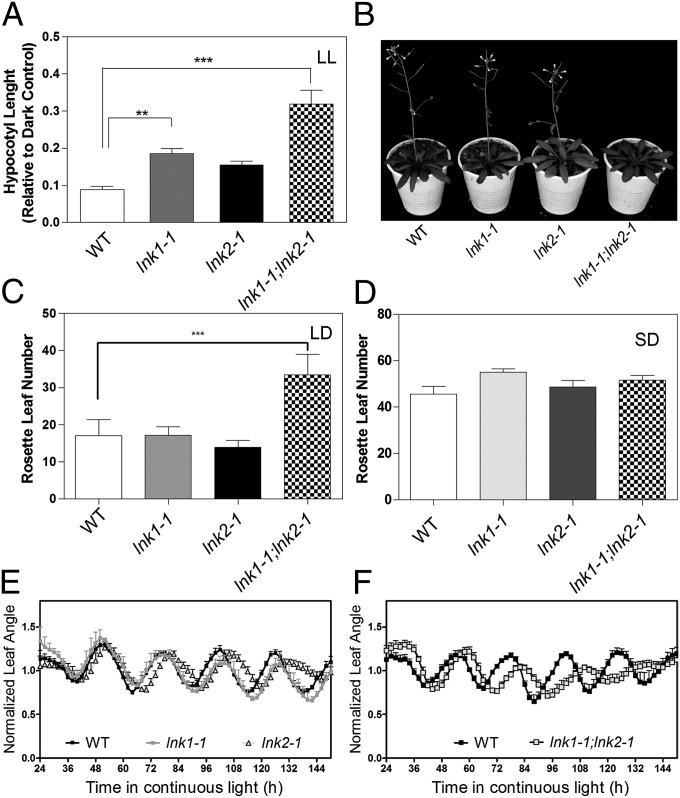
Fig. 2.
Physiological characterization of LNK1 and LNK2. (A) Hypocotyl length of WT, lnk1, lnk2, and lnk1;lnk2 mutant seedlings grown under continuous white light (LL) (n = 6 replicates of 10 seedlings each). (B) LNK1 and LNK2 control the floral transition in plants grown under LD (16-h light/8-h dark) conditions. (C and D) Flowering time measured as the number of rosette leaves at bolting in LD (C) and SD (D) conditions (8-h light/16-h dark). ANOVA followed by a Tukey´s multiple comparison test was used to evaluate the statistical significance of differences observed between genotypes. Error bars indicate +SEM (***P < 0.001, *P < 0.05). (E and F) Circadian rhythms of leaf movement in continuous light (n = 7). Plants were grown under LD cycles and then transferred to constant light and temperature conditions. Error bars indicate +SEM. Open and hatched boxes indicate subjective day and subjective night, respectively.