Figure 1.
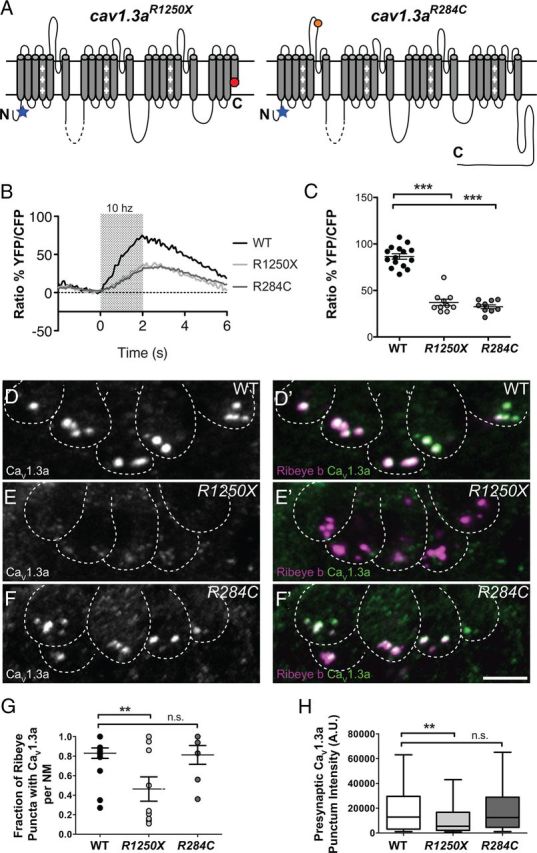
Characterization of CaV1.3a channel localization and activity in cav1.3a mutants. A, Diagrams representing the secondary structure of the α-pore-forming subunit CaV1.3a. Each diagram represents the expected protein resulting from the genetic lesions in each cav1.3a mutant. The position of the antibody epitope is denoted by a blue star. B, Mechanically evoked Ca2+ responses in WT and cav1.3a mutants at 5 dpf in response to a 2 s, 10 Hz alternating square waveform. Each trace represents the average response of hair cells from four NMs. C, Scatter plot depicts the average Ca2+ response per NM in WT and cav1.3a mutants. n ≥ 4 fish and n ≥ 10 NMs per genotype. Error bars are SEM. ***p < 0.001, defined by the Dunnett's multiple comparison test. D–F, Representative labeling of CaV1.3a clusters in cross-sections of NMs in 5 dpf WT (B), R1250X (C), and R284C (D) larvae. Dashed lines outline hair cells. Ribeye b label in merged images indicates CaV1.3a clusters localized to synaptic ribbons. Scale bar, 3 μm. G, Fraction of Ribeye with localized CaV1.3a clusters within NMs (5 dpf). Each data point represents the NM at position 2 along the trunk (NM2) in individual larvae. Error bars are SEM. **p < 0.01, defined by the Dunnett's multiple comparison test. H, Box plots of the fluorescent intensities of presynaptic CaV1.3a. These plots show the median value (horizontal bar), the upper and lower quartiles (box), and the range (whiskers). Whiskers indicate the 10th and 90th percentiles. **p < 0.01, defined by the Dunn's multiple comparison test.
