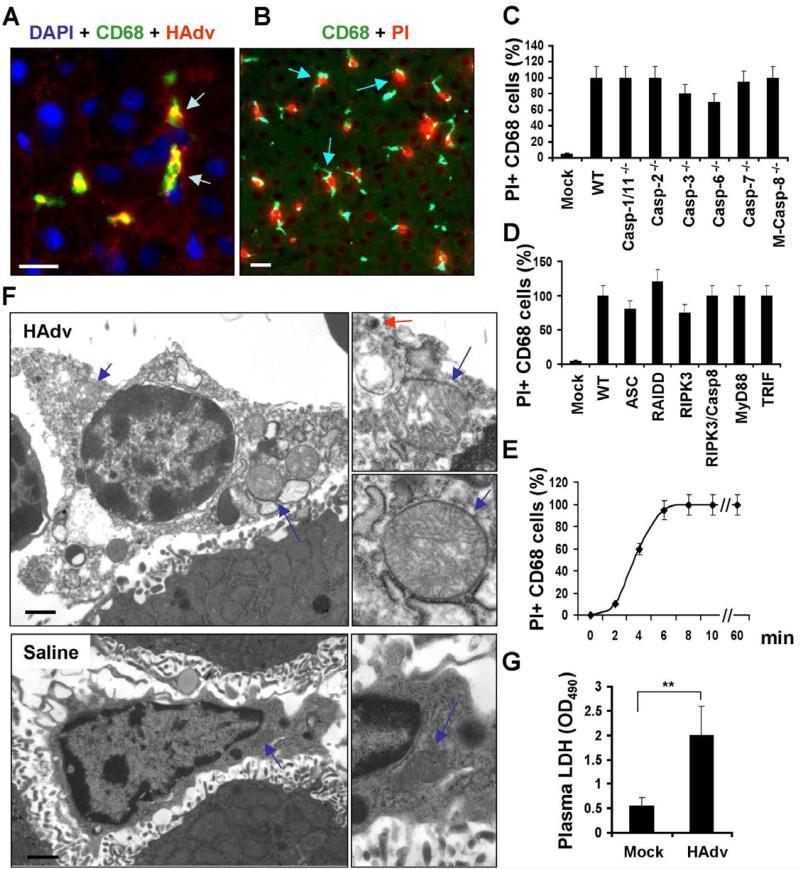
Figure 1. HAdv triggers necrotic type of macrophage death in vivo, independently of caspase-1, caspase-8, and RIPK3.
(A) Confocal microscopy analysis of HAdv particle distribution in liver parenchyma revealed accumulation of the virus (red, indicated by arrows) in CD68+ resident macrophages (green). Cell nuclei were strained with DAPI (blue). N = 8. The scale bar is 10 μm. (B) CD68+ liver macrophages (green) become propidium iodide-permeable (red, indicated by arrows) after interaction with HAdv. N = 8. The scale bar is 10 μm. (C-D) The percentage of PI-permeable CD68+ cells in the liver parenchyma of indicated gene-deficient mice 60 min after challenge with HAdv. Error bars represent standard deviation of the mean. M-Casp-8-/- - mice with macrophage-specific ablation of Caspase-8. N = 8. (E) Kinetics of plasma membrane integrity loss by CD68+ macrophages in the livers of wild type mice after challenge with HAdv. N = 5. (F) Electron microscopy analysis of ultrastructural changes in liver macrophages 15 minutes after challenge with HAdv in vivo. Right panels in show the high-power images of mitochondria (blue arrows) and the virus (red arrow). The scale bar is 2 μm. N = 5. (G) Plasma LDH levels in mice mock-infected with saline or infected with HAdv 30 min post infection. N = 5, ** P < 0.01.