Figure 11.
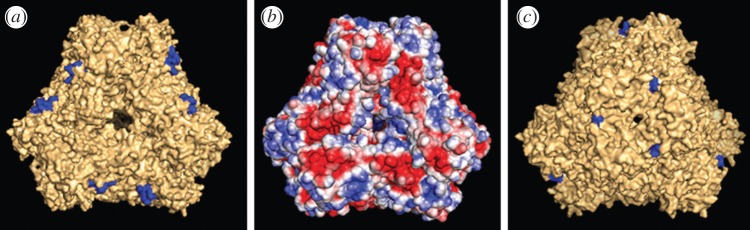
Surface rendering of the MHJ_0125 dodecameric structure showing the position of the heparin-binding consensus-like motif (a) and the C-terminal lysine residue likely to be involved in binding plasminogen (c). The surface potential of the dodecamer (rotated to look down the axis of the large pore) demonstrates that the heparin-binding motif (rich in lysine residues) confers a positive charge on these regions of the molecule's surface (b).
