Figure 9.
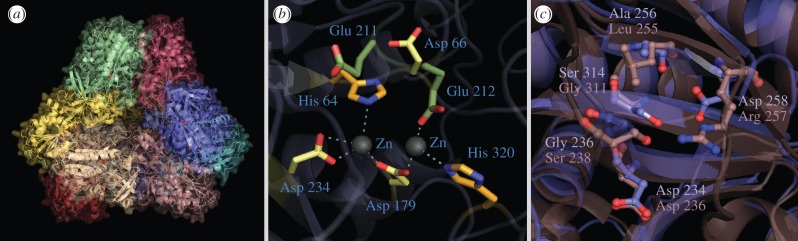
Molecular modelling of MHJ_0125. (a) A cartoon rendering of a comparative model of the MHJ_0125 dodecamer based on the tetrahedral crystal structure of P. horikoshii TET protease. Individual subunits are coloured. (b) A stick representation of the MHJ_0125 active site displaying residues involved in co-ordination of the metal ions (Zn2+ in this case) and substrate catalysis. Two zinc ions (Zn2+) per subunit have been modelled into the active sites of the complex (red spheres). (c) Structure of the substrate-binding (S1) pocket of MHJ_0125 (blue) overlaid with the S1 pocket of PepA glutamyl aminopeptidase from S. pneumoniae. PepA contains an arginine residue (Arg257) that confers a positive charge on one end of the S1 pocket that is believed to position adjacent to the carboxylate group of the glutamic acid substrate. Curiously, this residue is substituted for Asp258 in MHJ_0125; however, it appears that the side chain does not protrude far enough into the S1 pocket to confer a negative charge at this position.
