Figure 6.
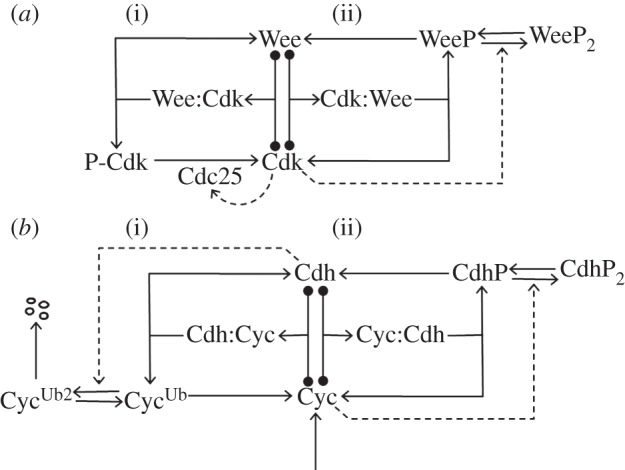
Wiring diagrams for other cell cycle transitions. (a) The G2/M transition. Wee1 is a protein kinase that phosphorylates and inactivates Cdk1 (i). Simultaneously, active Cdk1 (complexed with cyclin B) phosphorylates Wee1 on multiple sites in a typical SIMM motif (ii), where Wee1 functions as a stoichiometric inhibitor of Cdk1 as well as a substrate. Cdc25, the phosphatase that dephosphorylates P-Cdk1, is activated by multi-site phosphorylation catalysed by active Cdk1. (b) Mitotic exit. Cdh1 (in combination with the APC) stabilizes G1 phase of the cell cycle by poly-ubiquitinating cyclin B (i). Simultaneously, active Cdk1:CycB phosphorylates Cdh1 on multiple sites (ii). Both sides of the interaction have SIMM topology, but it is not known if either of the ‘substrates’ serves also as a ‘stoichiometric inhibitor’ of the enzyme.
