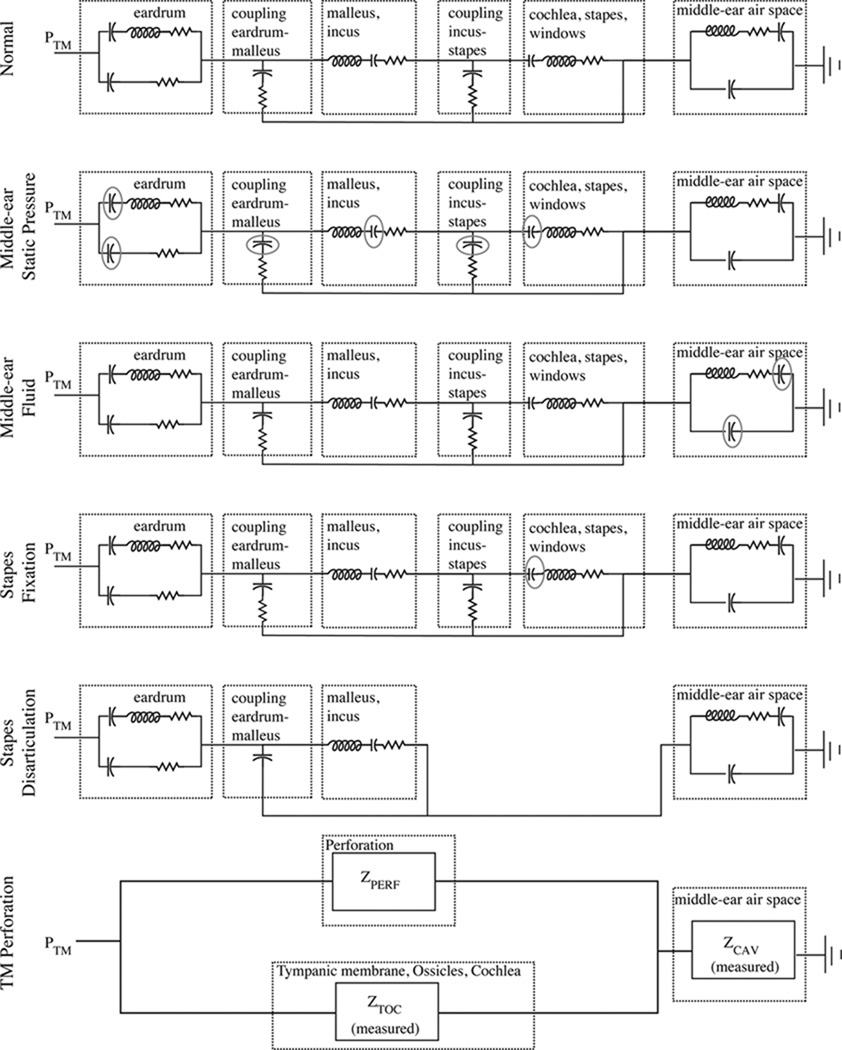
Figure 10.
Electric-circuit analog models that represents structures of the middle ear (Kringle-botn, 1988). Outlined sections illustrate the functional representations of the model, and the exact model-element values are described in Kringlebotn (1988). Modifications from Kringle-botn’s model for the normal ear are described within the text. PTM is the pressure at the tympanic membrane, and the power reflectance ℛ and transmittance T are calculated from the input impedance at the tympanic membrane. The acoustic quantities of sound pressure and volume velocity are analogous to the electric quantities of voltage and current. Acoustic losses are represented as resistors, compliances as capacitors, and masses as inductors.