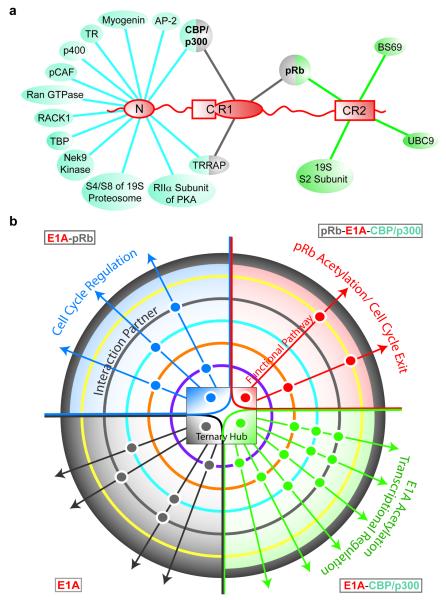
Figure 4. E1A functional complexity achieved through binding promiscuity.
a, Interactions of the N-terminal, CR1 and CR2 motifs of E1A with cellular proteins. Interactions mediated by the CR3 and CR4 regions of E1A5 are not shown. b, Allosteric modulation of signaling pathways by interactions of the E1A-CBP/p300-pRb “ternary hub”. This hub, represented by a central phase diagram, has four E1A states: free E1A, E1A-pRb, E1A-CBP/p300, and ternary complex (gray, blue, green and red quadrants, respectively). Colored concentric circles surrounding the hub represent additional protein partners with different interaction propensities for individual hub states. Each positive interaction is represented by a dot, colored by hub state, and positioned based on the interaction partner. These ternary hub interactions with different sets of partners result in multiple functional pathways, the control of which may be achieved by modulating the central E1A-CBP/p300-pRb hub equilibria.