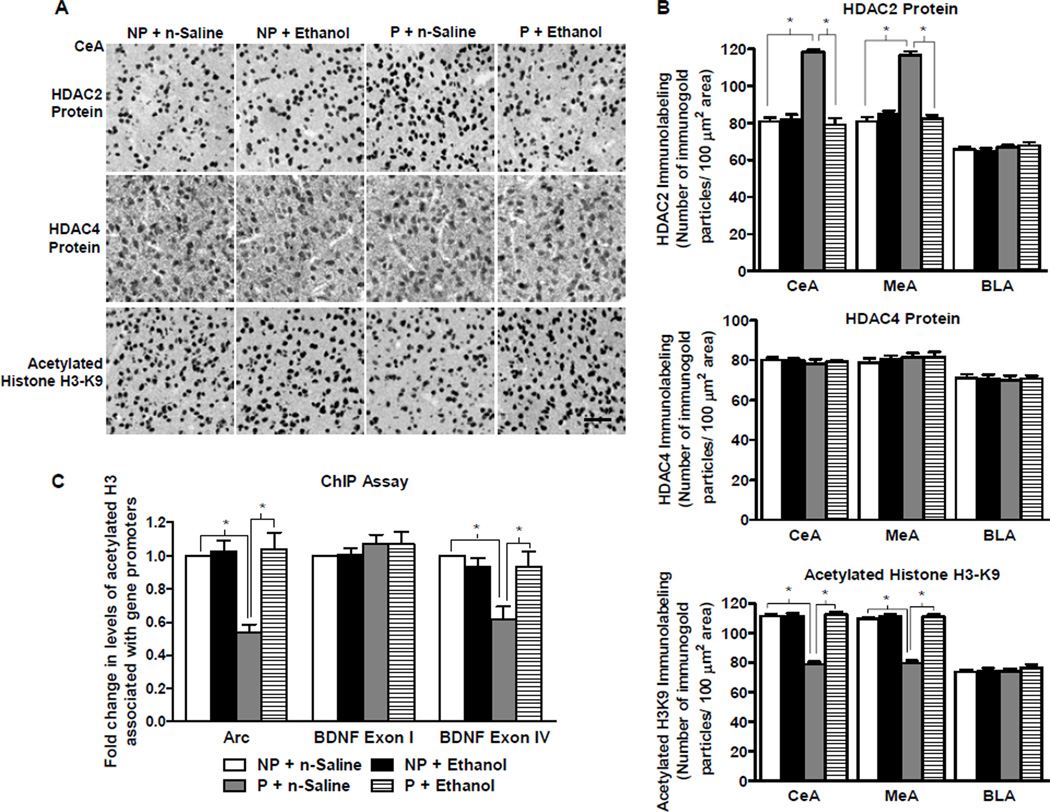
Figure 2. The effect of acute ethanol exposure on amygdaloid expression of histone deacetylases (HDAC) 2 and 4, and histone H3-K9 acetylation in P and NP rats.
A. Representative low-magnification photomicrographs (Scale bar = 50 µm) of gold-immunolabeling of HDAC2, HDAC4, and H3-K9 acetylation in the central nucleus of amygdala (CeA) of alcohol-preferring (P) and -nonpreferring (NP) rats treated with either n-saline or ethanol (1 g/kg).
B. HDAC2 protein levels, but not HDAC4 protein levels, were innately higher in the CeA (Group × treatment, F1, 20 = 64.8, p<0.001) and MeA (Group × treatment, F1, 20 = 84.2, p<0.001), but not BLA, of P rats in comparison to NP rats. Acute ethanol exposure reduced HDAC2 expression, but did not modulate HDAC4 expression, in the CeA and MeA of P rats, but not NP rats. Histone H3-K9 acetylation was also significantly different between the groups in the CeA and MeA, but not BLA. Acetylated H3-K9 levels were lower in the CeA (Group × treatment, F1, 20 = 104.7, p<0.001) and MeA (Group × treatment, F1, 20 = 101.7, p<0.001), but not BLA, of P rats in comparison to NP rats at baseline. Treatment with acute ethanol increased levels of histone H3-K9 acetylation in the CeA and MeA of P rats, but not NP rats. Values are represented as the mean ± SEM of the number of immunogold particles per 100 µm2 area from 6 rats per group. *Significantly different from their respective control groups (p<0.001; two-way ANOVA followed by post hoc analysis by Tukey’s test).
C. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) analysis identified significant differences between the groups for acetylated histone H3-K9/14 associated BDNF exon IV and Arc, but not BDNF exon I (BDNF exon IV: group × treatment, F1, 20 = 8.6, p<0.01; Arc: group × treatment F1, 20 = 14.8, p<0.001). The levels of acetylated histone H3-associated gene promoter of BDNF exon IV and Arc, but not BDNF exon I, were lower in tissue homogenates composed primarily of CeA and MeA in P rats than in NP rats at baseline. Treatment with acute ethanol (1 g/kg) increased amygdaloid levels of acetylated histone H3 associated BDNF exon IV and Arc, but not BDNF exon I, in P rats, but not NP rats. Values are represented as the mean ± SEM of the fold change of acetylated histone levels associated with the aforementioned genes normalized to the NP + n-saline group and derived from 6 rats per group. *Significantly different from their respective control groups (p<0.01–0.001; two-way ANOVA followed by post hoc analysis by Tukey’s test).