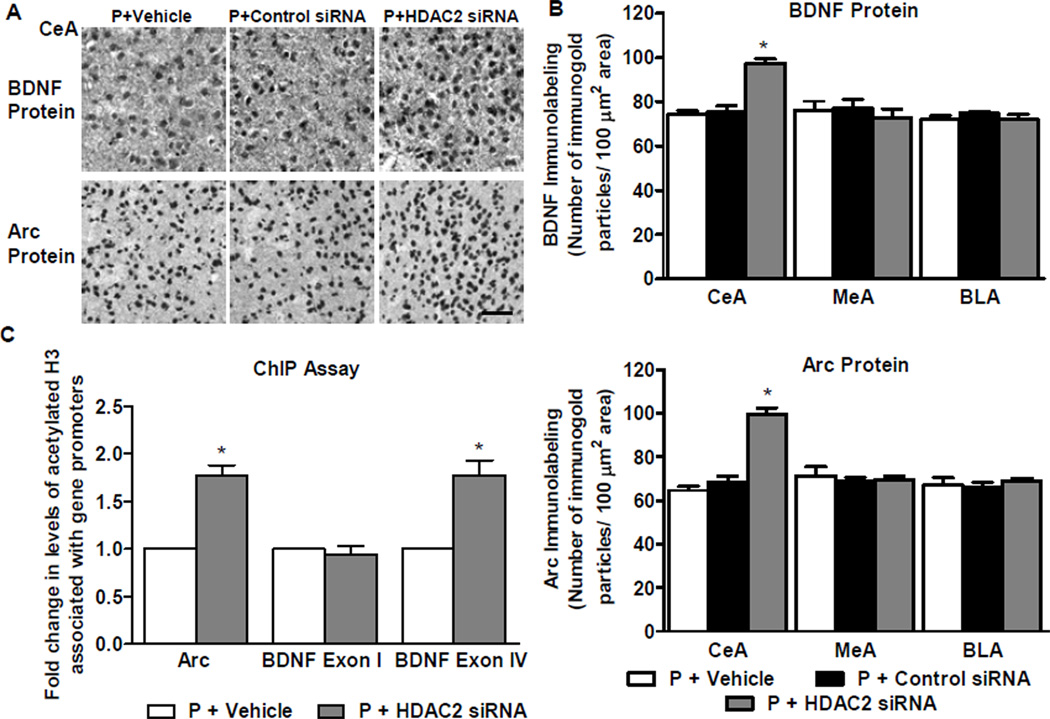
Figure 5. Effects of HDAC2 siRNA infusion into the CeA on protein levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated (Arc) protein and on acetylated histone H3 levels of BDNF exons I, IV and Arc genes in the amygdala of P rats.
A. Representative low-magnification photomicrographs showing immunohistochemical staining (gold immunolabeling) for BDNF and Arc protein in CeA. Scale bar = 50 µm.
B. Analysis of BDNF and Arc protein levels identified a significant difference between the vehicle-, HDAC2 siRNA-, and control siRNA-infused P rat groups in the CeA, but not MeA or BLA (BDNF: CeA, F2,11 = 34.5, p<0.001; Arc: CeA, F2,14 = 57.8, p<0.001). HDAC2 siRNA infusion into CeA resulted in an increase of BDNF and Arc protein in the CeA, but not MeA or BLA, of P rats in comparison to those infused with vehicle or control siRNA. Values (number of the immunogold particles per 100 µm2 area) are represented as the mean ± SEM and derived from 4–6 rats per group. *Significantly different from control groups (p<0.001; one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc analysis by Tukey’s test).
C. ChIP analysis revealed that HDAC2 siRNA infusion increased the levels of acetylated histone H3-K9&14 of BDNF exon IV and Arc, but not BDNF exon I. Values represent mean ± SEM derived from 6 P rats per group. *Significantly different from vehicle-infused P rats (p<0.001; Student’s t-test).