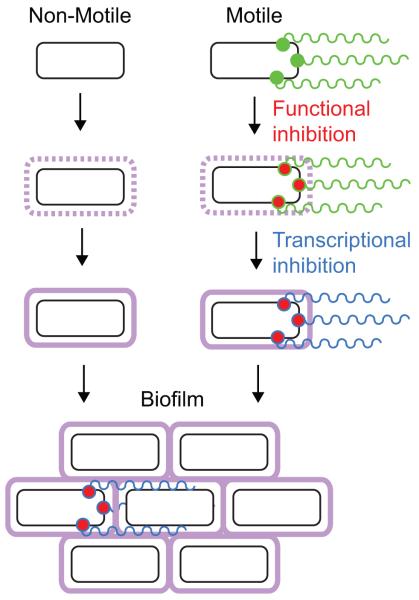
Figure 2. General steps of the motility to biofilm transition.
We propose a model for biofilm formation that incorporates two cell types: those that are non-motile and those that are initially motile. Flagella that are rotating are labeled in green, functional inhibition of the flagellum is labeled in red, decreased transcription of flagella genes is denoted by labeling the flagellum blue, and the extracellular matrix is shown in purple. Non-motile cells increase transcription of and synthesize the extracellular matrix components (purple), while motile cells first inhibit motility functionally at the flagella basal body (red), then decrease transcription of flagella genes (blue) while increasing expression of the extracellular matrix components (purple). Finally, both types of cells form a biofilm together.