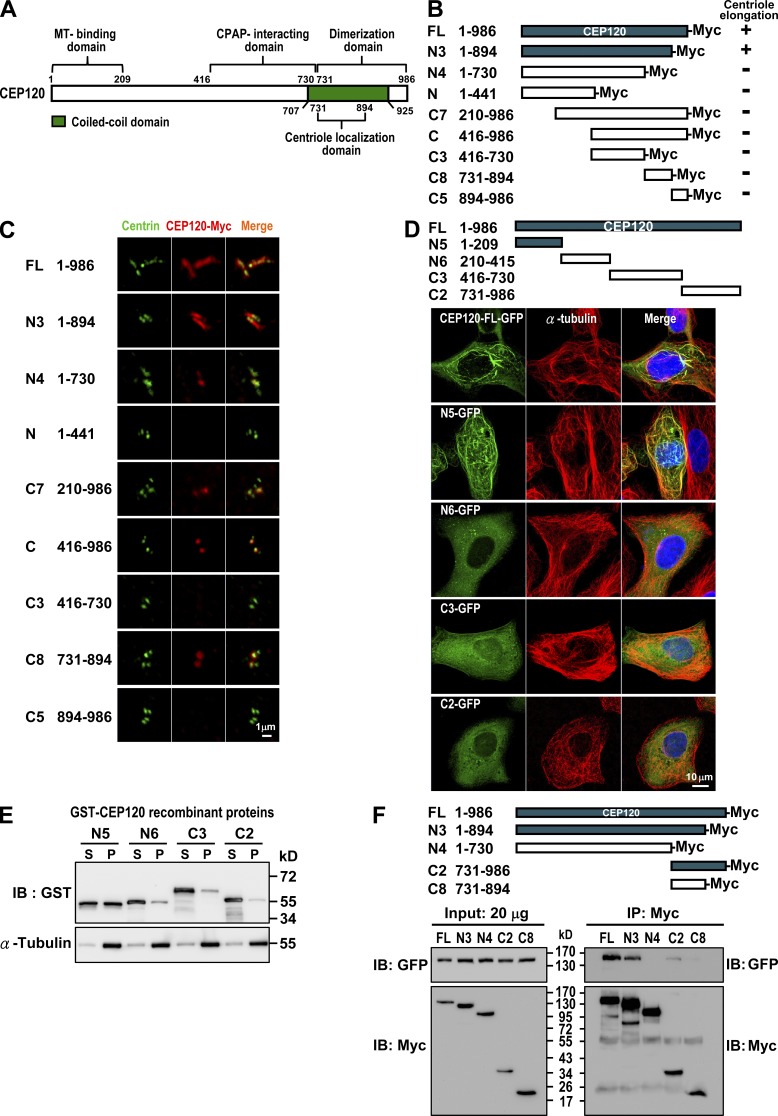
Figure 4.
Mapping the functional domains of CEP120. (A) Summary of CEP120 functional domains. (B and C) Mapping the region required for CEP120-induced centriole elongation. U2OS cells were transiently transfected with various CEP120-Myc–truncated constructs (B) and analyzed by confocal fluorescence microscopy using antibodies against centrin and Myc (C). (D and E) Mapping the MT-binding domain in CEP120. Various GFP-tagged CEP120-truncated constructs (D) were transiently expressed in U2OS cells and analyzed by confocal fluorescence microscopy. (E) A MT cosedimentation assay was performed by incubating various recombinant GST-CEP120 proteins with purified tubulins and Taxol (20 µM). The supernatants (S) and pellets (P) were analyzed by immunoblotting. (F) Mapping the dimerization domain in CEP120. HEK 293T cells were cotransfected with various Myc-tagged CEP120-truncated constructs and a full-length CEP120-GFP. 24 h after transfection, cell lysates were analyzed by immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies.