Figure 5.
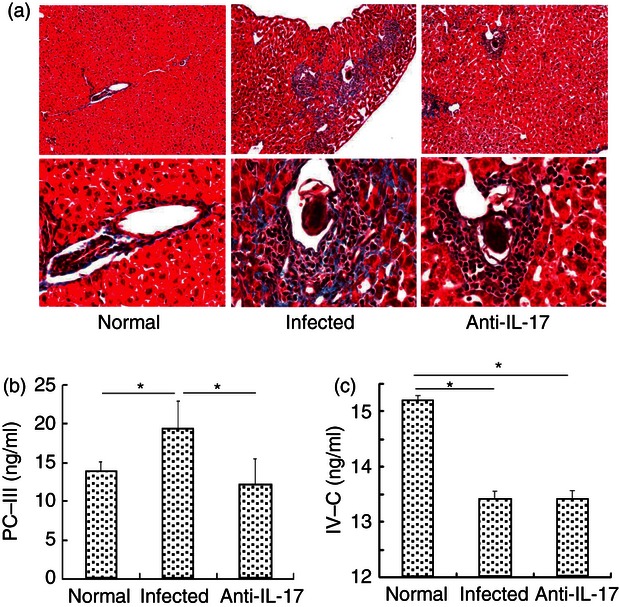
Reduction of hepatic fibrosing inflammation by anti-interleukin-17 (IL-17) monoclonal antibody (mAb) in vivo. Female C57BL/6 mice were divided into three groups, normal group, infected group and anti-mouse IL-17 mAb group. The infected and anti-IL-17 mAb groups were infected with 40 ± 5 cercariae of Schistosoma japonicum per mouse. For infected and group, 62·5 μg of control IgG mAb or anti-IL-17 mAb per mouse were administered intraperitoneally every three days, for a total of four times, respectively. Six weeks after the infection, the mice were killed. (a) Livers were flushed with 0·01 m PBS three times, fixed in 10% formalin, embedded in paraffin, and sectioned. Sections of the liver of normal, control IgG mAb and anti-IL-17 mAb mice were examined by Masson's trichrome staining (× 100 for upper panels, × 400 for lower panels). (b and c) Levels of pro-collagen type III (PC-III) and type IV collagen (IV-C) in the serum of three groups were detected by ELISA (*P < 0·05, the error bars indicate SD).
