Figure 1.
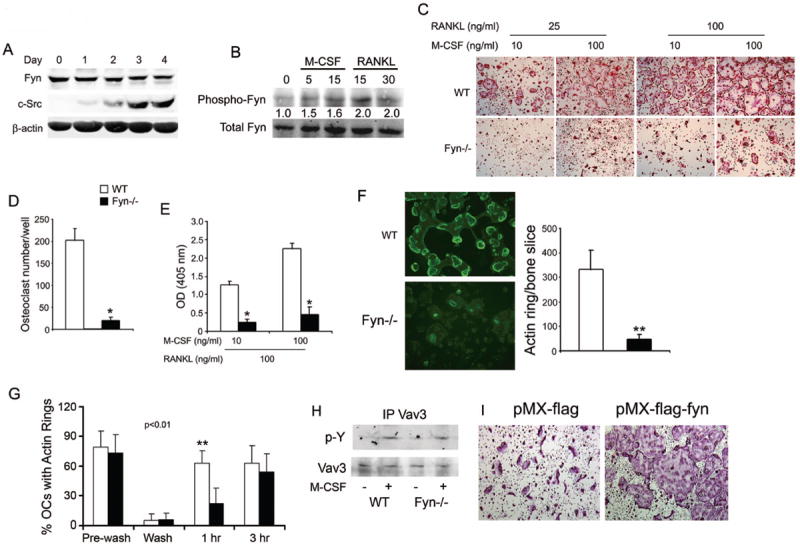
Fyn deficiency impairs osteoclast formation and spreading. (A) WT BMMs were cultured in M-CSF and RANKL. Lysates were collected daily for 4 days and immunoblot performed for Fyn and c-Src content. β-actin serves as loading control. B) WT BMMs plated in M-CSF were cytokine- and serum-starved overnight and then exposed to M-CSF or RANKL with time dictated by established signaling kinetics. Fyn immunoprecipitates were immunoblotted for total and phosphorylated Fyn. Blot intensity was densitometrically quantitated and the phospho-Fyn/total Fyn ratio normalized to time 0. (C-E) WT and Fyn-/- BMMs were cultured with M-CSF and RANKL. (C) Cells were stained for TRAP activity at day 5. (D) Statistical analysis of the number of WT and Fyn-/- TRAP-expressing multinucleated giant cells/well at day 5. (E) TRAP activity determined by ELISA at day 4. (F) WT and Fyn-/- BMMs were cultured on bone with M-CSF and RANKL. (left panel) After 5 days, the cells were fixed and stained with FITC-phalloidin to visualize actin rings. (right panel) Statistical analysis of the number of WT and Fyn-/- actin rings/bone slice at day 5. (G) Mature WT and Fyn-/- osteoclasts cultured on bone slices, were washed with cytokine-free cold medium to dissociate actin rings. The cells were then incubated with RANKL for 1 or 3 hrs and the percentage of osteoclasts, which had re-formed actin rings, determined. (H) WT and Fyn-/- BMMs were cytokine starved for 6 hrs prior to a 5 min exposure to M-CSF or carrier. Lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Vav3 mAb and the product immunoblotted for phosphotyrosine and Vav3 content. (I) Fyn-/- BMMs were retrovirally transfected with vectors bearing FLAG or FLAG- Fyn. OCs were generated by 5 days in RANKL and M-CSF. (*p< 0.01, **p< 0.005).
