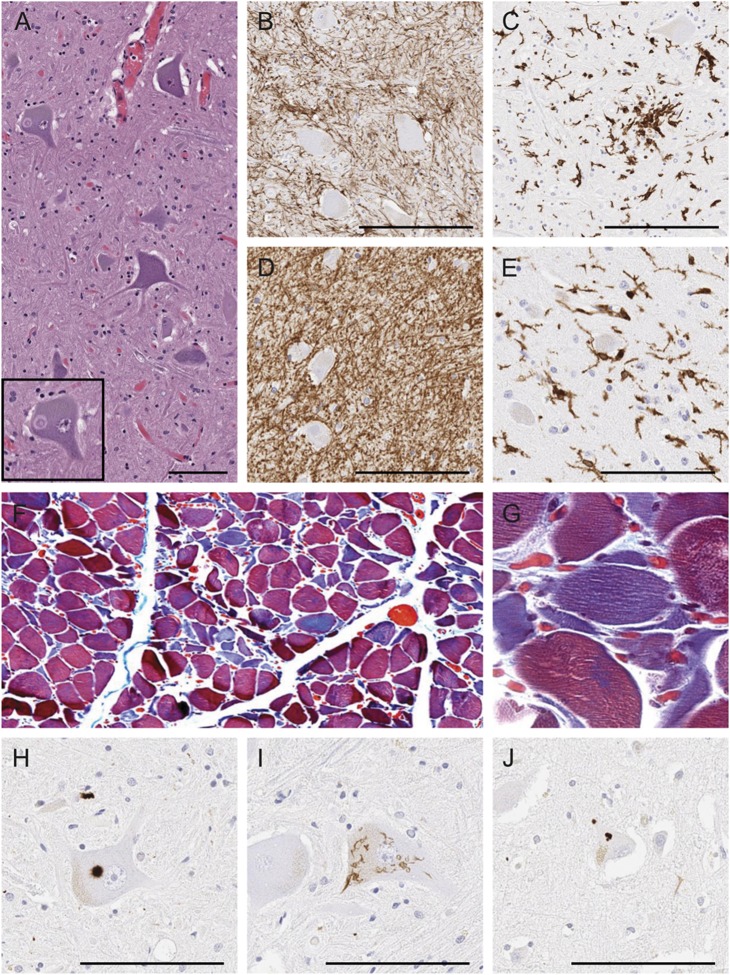
Figure 2. Pathologic assessment of case 1.
(A) Hematoxylin & eosin staining of anterior horn spinal cord tissue reveals Lewy body–like hyaline inclusions (inset). (B and C) Immunohistochemical staining of spinal cord tissue for GFAP (B) and IBA1 (C) shows gliosis. (D and E) Immunohistochemical staining of medulla for GFAP (D) and IBA1 (E) shows moderate gliosis. (F and G) Erector spinae muscle with trichrome stain demonstrates neurogenic atrophy of muscle fibers. (G) Higher magnification shows a cluster of angulated fibers. (H–J) Immunohistochemical staining for phosphorylated TDP-43 reveals Lewy body–like inclusions in anterior horn cell (H), skein-like inclusions in anterior horn cell (I), and neuronal cytoplasmic inclusions in Betz cells of motor cortex (J). Bar represents 100 μm. GFAP = glial fibrillary acidic protein; IBA1 = ionized calcium-binding adaptor molecule 1; TDP-43 = TAR DNA-binding protein 43.