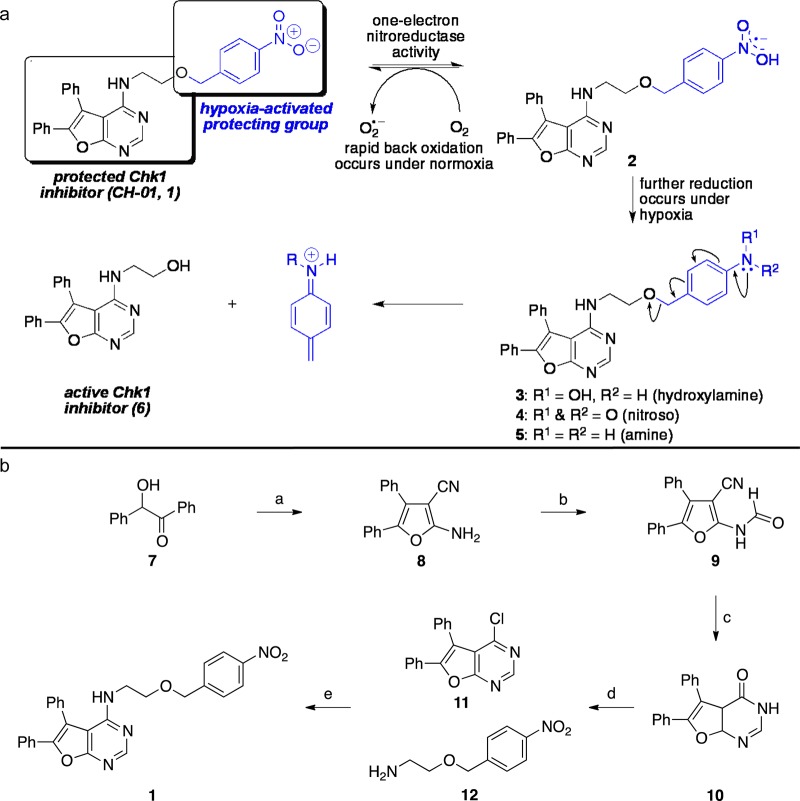
Figure 2.
The concept of the hypoxia-activated Chk1 inhibitor CH-01 and its synthesis. (a) Attachment of the 4-nitrobenzyl group to the terminal hydroxyl group renders the Chk1 inhibitor 6 inactive. Under hypoxic conditions, the nitro group is reduced forming an electron-donating substituent, which ejects the active Chk1 inhibitor 6. (b) Reagents and conditions: (a) malononitrile, Et2NH, dioxane, reflux, 16 h, 75%; (b) acetic formic anhydride, 85 °C, 6 h; (c) neat, 220 °C, 30 min, 51% over two steps; (d) POCl3, 55 °C, 2 h, 81%; (e) Et3N, DMF, 80 °C, 6 h, 93%.