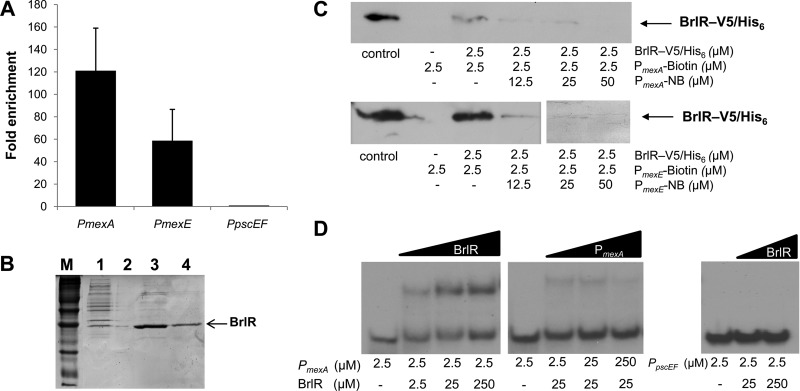
Fig 2.
BrlR binds to the promoters of mexAB-oprM and mexEF-oprN. (A) Fold enrichment of the promoter sequences of mexA and mexE by ChIP compared to control (ChIP carried out in the absence of BrlR-V5/His6) as determined by qPCR. (B) Purification of BrlR-V5/His6. Lane M, protein marker; lane 1, lysate obtained from E. coli BL21/pET-brlR-V5/His6; lane 2, blank; lanes 3 and 4, eluates (fractions 1 and 2) obtained from Ni-NTA resin. Purified protein shown in lane 4 was used for EMSA and streptavidin binding assays. The molecular mass of tagged BrlR is 33 kDa. (C) Streptavidin magnetic bead binding assay demonstrating binding of V5/His6-tagged BrlR protein to 2.5 pmol of biotinylated PmexA and PmexE. Nonbiotinylated PmexA and PmexE (PmexA/mexE-NB) were used as specific competitor DNAs in 5-, 10-, and 20-fold excesses. BrlR binding to PmexA and PmexE was detected by immunoblot analysis using anti-V5 antibodies. +, presence of PmexA/mexE-biotin or PmexA/mexE-NB; −, absence of PmexA/mexE-biotin or PmexA/mexE-NB. Control, purified BrlR-V5/His6. (D) First gel, EMSA demonstrating BrlR binding to the 159-bp-long PmexA promoter region. BrlR concentrations were increased 10-fold over three concentrations. Second gel, BrlR binding to PmexA was outcompeted by increasing the concentration of unlabeled PmexA competitor DNA. Third gel, BrlR binding to the 92-bp-long PpscEF promoter region used as a control was not detected regardless of the BrlR concentration used. All experiments were carried out in triplicate.