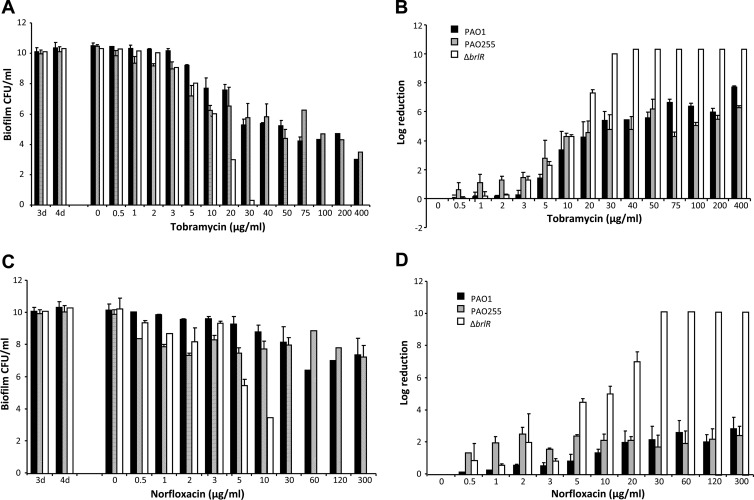
Fig 5.
MexAB-OprM and MexEF-OprN do not contribute to resistance to killing of P. aeruginosa biofilms. P. aeruginosa PAO1, PAO255, and ΔbrlR mutant biofilms were grown as 3-day biofilms and subsequently treated for 24 h under continuous-flow conditions before surviving cells were recovered and enumerated. (A) Biofilm susceptibility to tobramycin as determined by viable counts (CFU). Viable ΔbrlR mutant cells were below the detection limit at the highest concentrations of tobramycin tested. (B) Biofilm susceptibility to tobramycin as determined by log reduction. Total killing of ΔbrlR biofilm cells was achieved at 40 μg/ml of tobramycin. In contrast, P. aeruginosa PAO1 and PAO255 biofilms maintained a steady level of persisting survivors at concentrations higher than 40 μg/ml of tobramycin. (C and D) Biofilm susceptibility to norfloxacin was determined similarly. Total killing of ΔbrlR biofilm cells was achieved at 30 μg/ml of norfloxacin, while PAO1 and PAO255 biofilms maintained a steady level of survivors through the highest concentrations tested. Error bars denote standard deviations.