Fig 2.
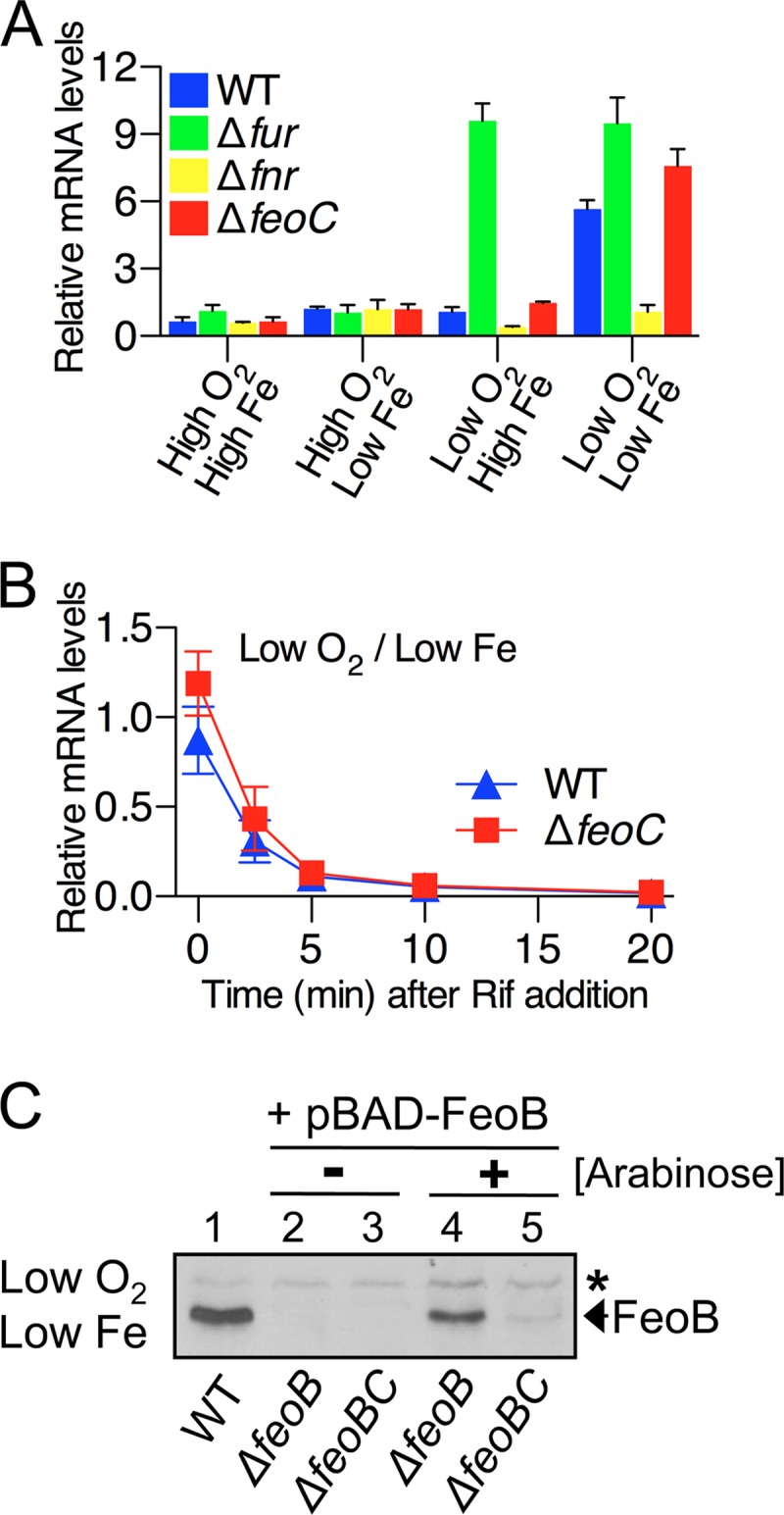
The FeoC protein contributes to cellular FeoB transporter levels at the posttranslational level. Salmonella strains were grown aerobically (high O2) or anaerobically (low O2) in LB (high Fe) or in LB containing 0.2 mM deferoxamine (low Fe). (A) qRT-PCR analysis determined mRNA levels of the feoB gene in wild-type (WT, 14028s), fur deletion (Δfur, JH352), fnr deletion (Δfnr, HK708), and feoC deletion (ΔfeoC, JH363) strains. (B) The stability of the feoB mRNA was examined in the wild-type (WT, 14028s) and feoC deletion (ΔfeoC, JH363) strains. RNA synthesis was inhibited with 200 μg/ml rifampin (Rif). qRT-PCR determined feoB mRNA levels in total RNA isolated at the indicated time points. Values (A and B) are the means and standard deviations (SD) of three independent experiments. (C) Immunoblot analysis determined FeoB protein levels in the wild-type (WT, 14028s), feoB deletion (ΔfeoB, JH362), and feoBC deletion (ΔfeoBC, HK715) strains. The JH362 and HK715 strains harbored the FeoB expression plasmid (pBAD-FeoB) and were grown with (+) or without (−) the inducer arabinose (60 μM). The band indicated with an asterisk corresponds to a protein displaying cross-reactivity against anti-FeoB antibody and serving as an internal loading control.
