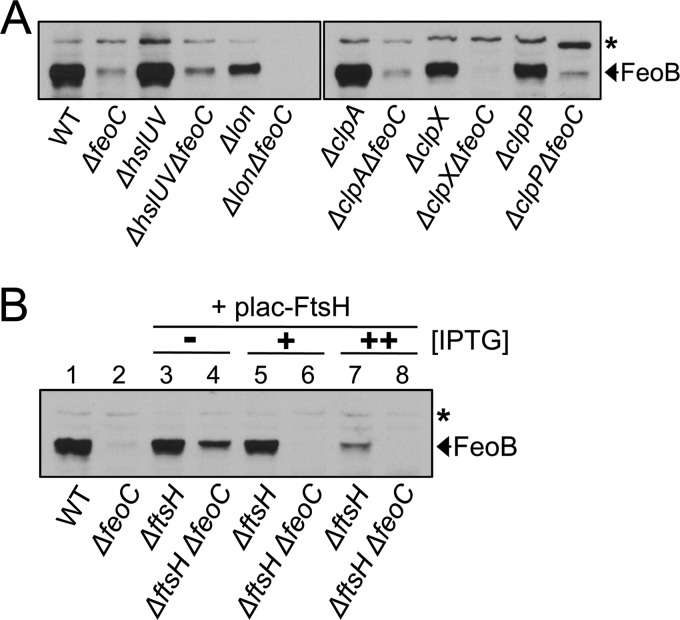
Fig 4.
Depletion of the FtsH protease enables high levels of FeoB in the absence of FeoC. Salmonella strains were grown anaerobically in LB medium with low iron (i.e., LB supplemented with 0.2 mM deferoxamine). Immunoblot analysis determined FeoB protein levels in the wild-type (WT, 14028s), feoC deletion (ΔfeoC, JH363), hslUV deletion (ΔhslUV, DN283), hslUV feoC deletion (ΔhslUV ΔfeoC, DN301), lon deletion (Δlon, DN282), lon feoC deletion (Δlon ΔfeoC, DN300), clpA deletion (ΔclpA, DN281), clpA feoC deletion (ΔclpA ΔfeoC, DN299), clpX deletion (ΔclpX, DN297), clpX feoC deletion (ΔclpX ΔfeoC, DN311), clpP deletion (ΔclpP, DN296), and clpP feoC (ΔclpP ΔfeoC, DN310) strains (A) and wild-type (WT, 14028s) and feoC deletion (ΔfeoC, JH363) strains and ftsH deletion mutants carrying (ΔftsH, HK333) or lacking (ΔftsH ΔfeoC, HK334) the feoC gene (B). Note that ftsH mutants harbored the FtsH expression plasmid (plac-FtsH). ftsH mutants were grown to saturation in the presence of the inducer IPTG (30 μM), and cultures diluted to OD600 values of approximately 0.01 were grown to OD600 values of approximately 0.5 with 30 μM (+) or 60 μM (++) IPTG or without (−) IPTG. The band indicated with an asterisk corresponds to a protein displaying cross-reactivity against anti-FeoB antibody and serving as an internal loading control.