Fig 6.
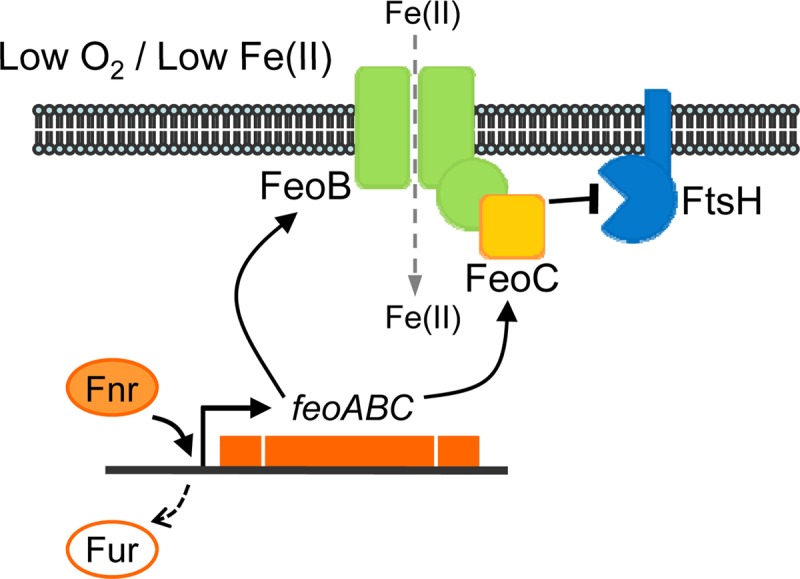
Model illustrating the role of FeoC in FeoB cellular levels. In Salmonella experiencing environmental conditions with low levels of oxygen and iron, Fur repression is relieved on the feo operon while Fnr promotes expression of the feoC mRNA (see Fig. S2 in the supplemental material) together with the feoB mRNA. The FeoB transporter is under proteolytic control by the membrane-bound FtsH protease. The FeoC protein binds to the cytoplasmic N-terminal domain of FeoB, which protects the FeoB transporter from FtsH-mediated proteolysis. Consequently, the FeoC protein leads to high cellular levels of the FeoB transporter, which enables Salmonella to take up Fe(II).
