Fig 1.
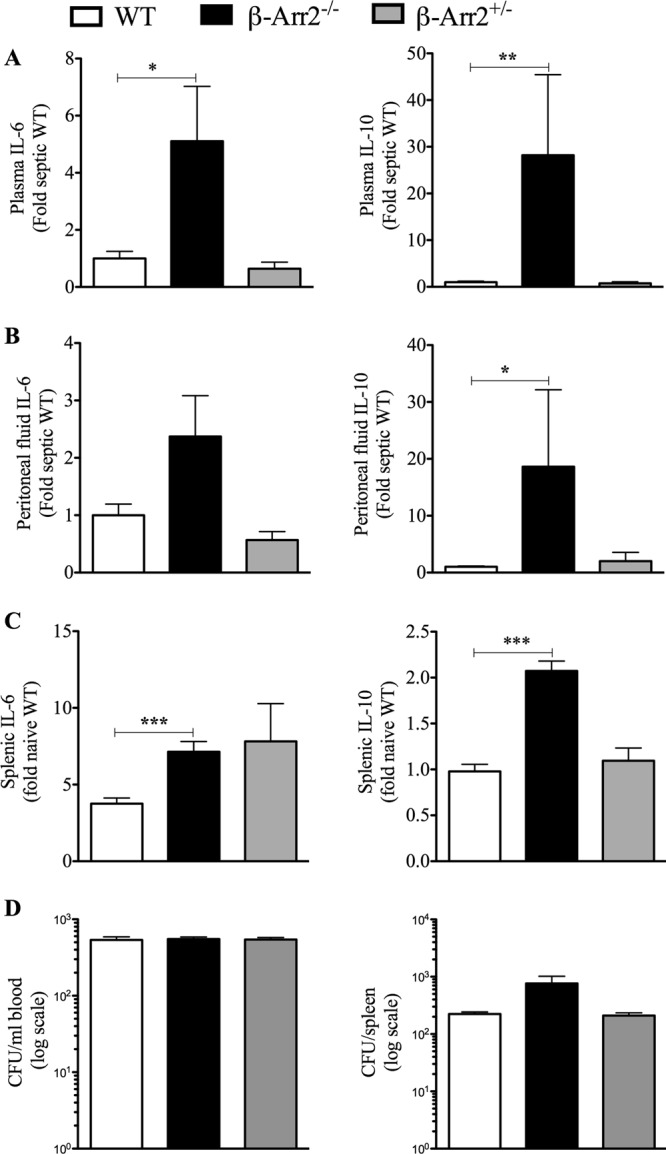
Cytokine production induced by polymicrobial injection is enhanced in β-arrestin-2 knockout mice. Wild-type (WT), β-arrestin-2 homozygous knockout (β-arr2−/−), and β-arrestin-2 heterozygous (β-arr2+/−) mice were intraperitoneally injected with polymicrobial culture. Six hours later, mice were euthanized and samples were collected as described in Materials and Methods. (A) Plasma cytokine. (B) Cytokines in splenic culture supernatant. Splenic cells were cultured at 5 × 106 cells/ml, and 24 h later, the supernatant was collected and assayed for the cytokine concentration. (C) Cytokines in peritoneal fluid. All concentrations were converted to fold change over septic WT for plasma and peritoneal fluid and over naive WT for spleen. Uninfected naive animals had undetectable levels of cytokines in plasma and the peritoneum. (D) Bacterial load in blood and spleen of infected mice, represented on a log scale. Uninfected naive mice had no bacterial load. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; compared to the WT using a t test or Mann-Whitney test. n = 3 for naive mice and 8 to 9 for septic mice for each genotype.
