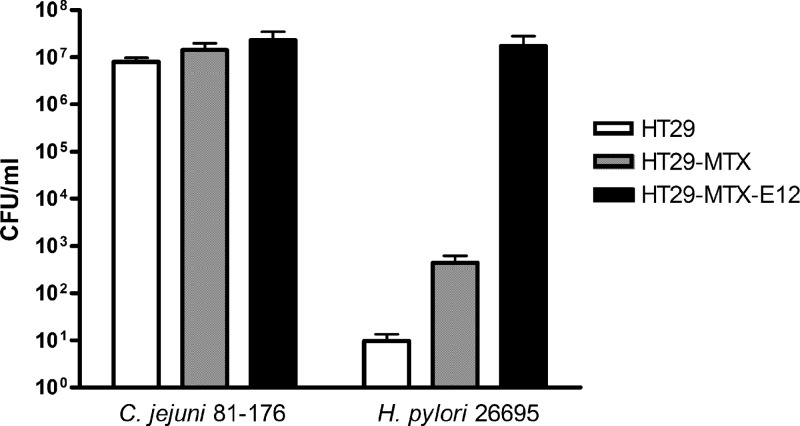
Fig 4.
Infection of HT29, HT29-MTX, and HT29-MTX-E12 cells by mucosal pathogens. The HT29-MTX subclone E12, with an adherent mucus layer, mucus-secreting HT29-MTX cells, and non-mucus-secreting HT29 cells were grown for 21 days on Transwell filters and were subsequently infected with C. jejuni or H. pylori organisms for 24 h. C. jejuni infected all cell lines. The numbers of C. jejuni organisms colonizing HT29-MTX and HT29-MTX-E12 cells were statistically significantly higher than the number colonizing HT29 cells (P < 0.05). In contrast, H. pylori colonized HT29-MTX-E12 cells and, to a much lesser extent, HT29-MTX cells but not HT29 cells. The data presented are means ± standard deviations for 3 replicate experiments (n = 9).