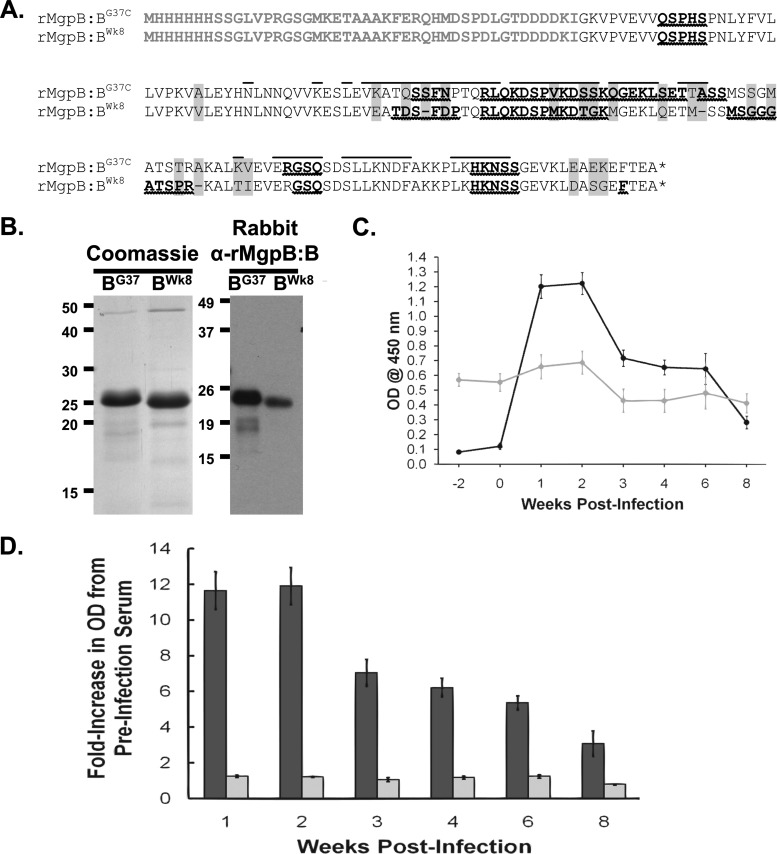
Fig 5.
Analysis of reactivity of primate serum to recombinant wild-type and variant MgpB region B peptides. (A) Amino acid sequences of the wild-type (rMgpB:BG37) and week 8 variant (rMgpB:BWk8) MgpB region B His-tagged recombinant peptides. Plasmid vector-associated amino acids, including the His tag, are shown in gray type. Amino acids that differ between the wild-type and week 8 peptides are indicated by gray background, and deleted amino acids are represented by a dash. The asterisk indicates the TGA codon that encodes stop in E. coli. Predicted linear B-cell epitopes are shown in bold type with wavy underlines; conformational B-cell epitopes for mycobacterial G37-C region B are overlined. His tag and vector-encoded amino acids were omitted from B-cell epitope predictions. (B) (Left) Coomassie blue stain of purified recombinant peptides. (Right) Reactivity of rabbit anti-MgpB region B (α-rMgpB:B) antibodies to purified recombinant peptides. Rabbit serum samples from animals immunized with a recombinant MgpB region B peptide consisting of amino acids 185 to 352 (Iverson-Cabral and Totten, unpublished data) were used at 1:1,000,000 and detected with HRP-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG secondary antibody diluted 1:1,000. (C) ELISA reactivity of primate serum to recombinant peptides over the course of infection. Reactivity of serum to rMgpB:BG37 (black circles) increased over time, while reactivity to rMgpB:BWk8 (gray circles) remained unchanged from the high background reactivity observed at weeks −2 and 0 (prior to infection). Primate serum samples were diluted 1:50 and detected with HRP-conjugated goat anti-human IgG secondary antibodies diluted 1:25,000. Data shown are averages of triplicate wells from a typical experiment repeated at least three times, and the error bars show standard errors. A no-antigen control was included for each plate, and this value was subtracted from the data shown. (D) ELISA data presented as fold increase compared to preinoculation values (average of week −2 and week 0). The graph shows the averages of five experiments, each with triplicate wells. Dark bars, wild-type peptide; light bars, week 8 variant peptide. Error bars indicate standard errors. The fold increase for reactivity to the rMgpB:BG37-C peptide was significantly different by Student's t test for weeks 1 through 6 (P < 0.001) and for week 8 (P = 0.0035) compared to preinoculation values.