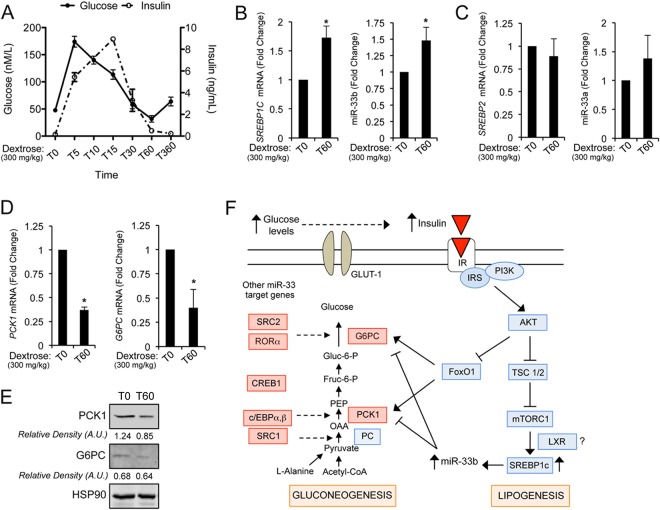
Fig 8.
SREBP1/miR-33b expression correlates inversely with PCK1 and G6PC levels in the liver of rhesus monkeys. (A) Blood glucose and insulin levels of rhesus monkeys fasted overnight and stimulated with glucose (dextrose, 300 mg/Kg). Measurements were performed after 5, 10, 15, 30, 60, and 360 min of intraperitoneal glucose injections. (B and C) qRT-PCR analysis of SREBP1c mRNA and miR-33b (B) and SREBP2 and miR-33a (C) expression levels in the liver of rhesus monkeys after 60 min of glucose stimulation. Data are presented as means ± SEM (n = 6). ∗, P ≤ 0.05 versus nontreated rhesus monkeys (T0). (D) qRT-PCR analysis of PCK1 and G6PC levels in the liver of rhesus monkeys after 60 min of glucose infusion. Data are presented as means ± SEM (n = 6). ∗, P ≤ 0.05 versus nontreated rhesus monkeys (T0). (E) Western blot analysis of PCK1 and G6PC expression levels in the liver of rhesus monkeys after 60 min of glucose stimulation. Data correspond to a representative experiment among three that gave similar results. (F) Schematic representation of the proposed regulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis by miR-33b. Red boxes represent the miR-33 target genes involved in hepatic glucose production.