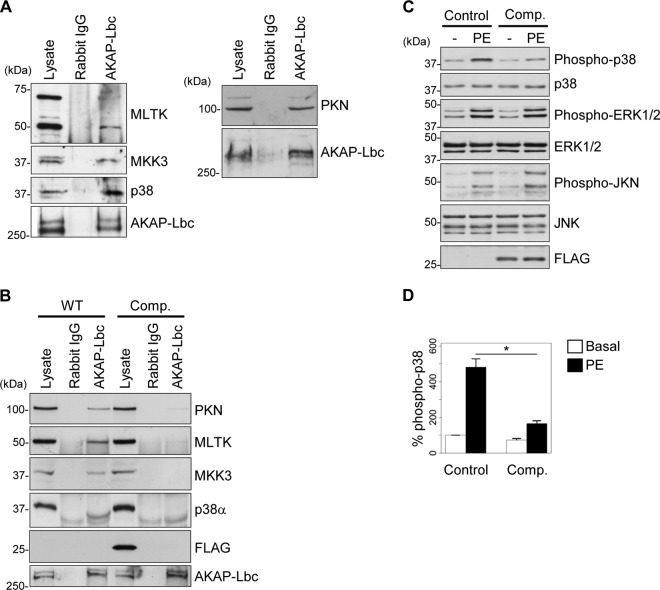
Fig 1.
AKAP-Lbc assembles a PKNα-based p38 activation complex in cardiomyocytes. (A) Rat NVM extracts were subjected to immunoprecipitation with either nonimmune IgGs or affinity-purified anti-AKAP-Lbc antibodies. Proteins in the lysates and immunoprecipitates were identified by immunoblotting using antibodies against PKNα, MLTK, MKK3, and p38α and AKAP-Lbc, as indicated. (B) Rat NVMs were infected with control lentiviruses or lentiviruses encoding the Flag-AKAP-Lbc-1570-1764 competitor fragment (Comp.). AKAP-Lbc was immunoprecipitated from infected NVM lysates as indicated in panel A. The presence of associated kinases was detected by immunoblotting using specific antibodies, as indicated. (C) Rat NVMs infected as indicated in panel B were serum starved and subsequently treated or not for 24 h with 10−4 M PE. The amounts of total and phosphorylated p38, ERK1/2, and JNK, as well as the expression of Flag-AKAP-Lbc-1570-1764, in the cell lysates were determined by immunoblotting using specific antibodies, as indicated. (D) Quantitative analysis of phosphorylated p38 was performed by densitometry. The amount of phospho-p38 was normalized to the total amount of p38. The results are presented as means and SEM of four independent experiments. Statistical differences were analyzed using the Student t test. *, P < 0.05 versus control cardiomyocytes treated with PE.