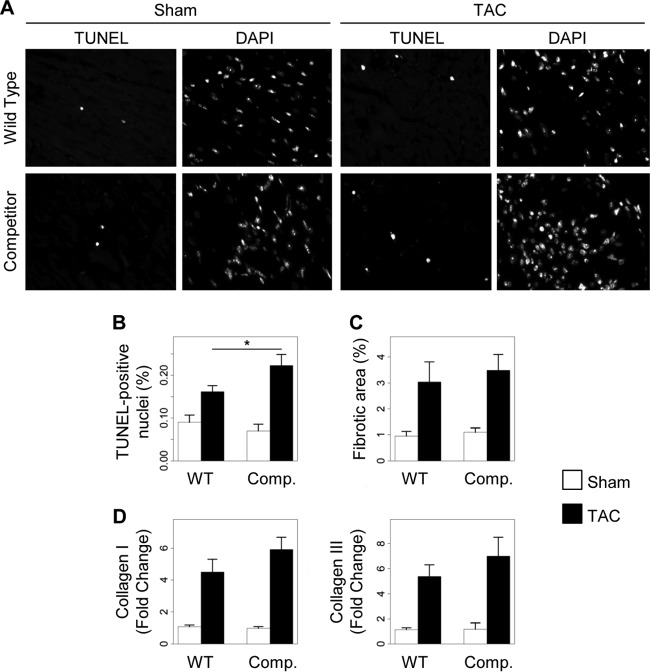
Fig 7.
Disruption of the AKAP-Lbc/p38 complex in cardiomyocytes enhances pressure overload-induced apoptosis. Transgenic (Comp.) and WT mice were subjected to 2 weeks of TAC or a sham operation. Histological analyses were done on transversal heart sections. (A) Representative TUNEL and DAPI stainings of transversal heart sections. (B) Quantification of apoptosis. The number of TUNEL-positive nuclei was normalized to the total number of nuclei per heart section. The data from two different heart sections were averaged for each mouse. WT-sham, n = 5; WT-TAC, n = 6; competitor-sham, n = 5; competitor-TAC, n = 8; P < 0.05 versus WT-TAC. (C) Quantitative assessment of fibrosis. Heart sections from the indicated groups of animals were stained with Masson's Trichrome. WT-sham, n = 6; WT-TAC, n = 7; competitor-sham, n = 5; competitor-TAC, n = 9. (D) The relative mRNA expression of collagen I and III in heart lysates from the indicated mouse groups was assessed by quantitative real-time PCR. Values were normalized to the expression of GAPDH and are presented as means and SEM. Statistical differences were analyzed using the Student t test. No statistically significant differences were found.