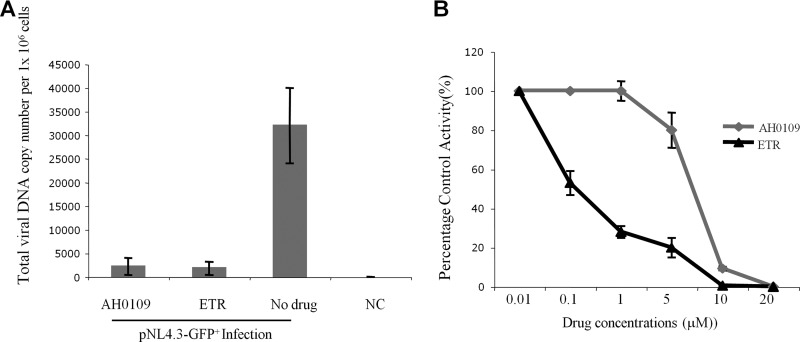
Fig 3.
AH0109 disrupts HIV-1 DNA synthesis by targeting reverse transcriptase. (A) 106 CD4+ C8166 T cells were infected with HIV-1 pNL4.3-GFP+ virus (MOI of 1) in the presence or absence of AH0109 (4.6 μM). An NNRTI, etravirine (ETR; 4.6 μM), was also used as a control. After 20 h of infection, the cells were collected, and DNA was isolated by using a QIAamp DNA blood minikit (Qiagen). The total HIV-1 DNA levels were measured by real-time Q-PCR analysis. (B) Effect of AH0109 on virion-associated reverse transcriptase activity. A colorimetric enzyme immunoassay that quantifies retroviral reverse transcriptase activity based on incorporation of digoxigenin- and biotin-labeled dUTP into DNA was used. Etravirine was included as a positive control. The percent control activity (%) indicates a ratio of reverse transcriptase activity in the presence of AH0109 or etravirine versus the absence of any compound. These data are means of results from three independent experiments and are expressed with the standard deviations.