Fig 2.
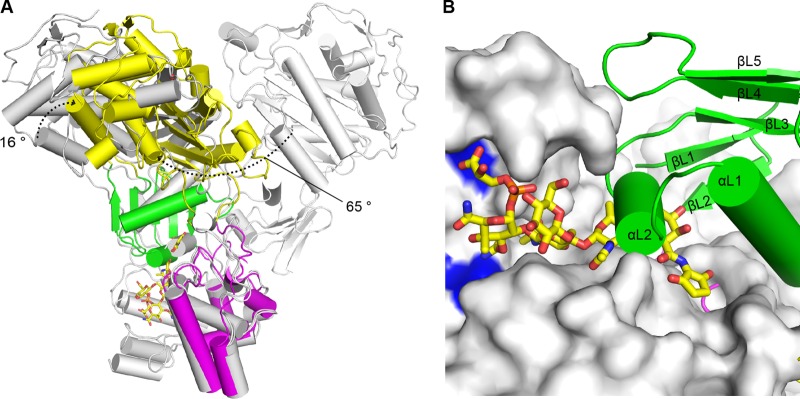
Interdomain flexibility of LmPBP4. (A) TP domain movement. The GT domains of LmPBP4 and those of SaPBP2 (PDB codes 2OLV and 3DWK) were superimposed. The structures of SaPBP2 are in gray for chain B of 2OLV and in cyan for chain A of 3DWK. The dotted arrows indicate the rotational movements of the TP domain. In this superposition, only two conformations of SaPBP2 are shown for clarity. (B) Blocking of the GT active site by the linker domain. The GT domain of the SaPBP2-moenomycin complex (PDB code 2OLV) overlaid on that of LmPBP4 is shown as a surface model, and the moenomycin is shown as a stick model with C atoms colored yellow. The catalytic glutamate residues are in blue. The linker domain of LmPBP4is presented as a ribbon model. The short αL1 helix (residues 310 to 316) of the linker domain occludes the GT active-site cleft, where the growing NAG-NAM polyglycan chain binds.
