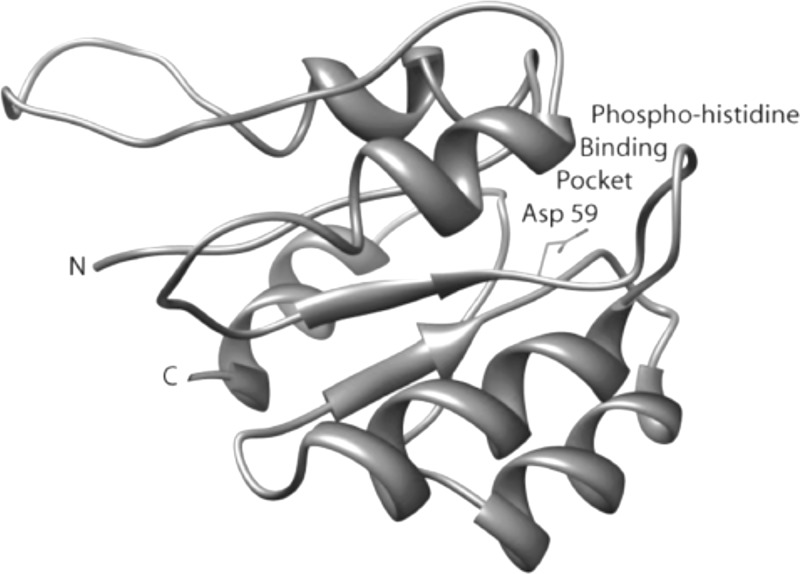
Fig 2.
Ribbon diagram of the homology-built model of the N-terminal domain of AgrA (AgrA_N). Residue Asp 59, shown in stick representation in a pocket on the surface of the protein, is phosphorylated by the histidine kinase AgrC, leading to activation of the C-terminal DNA-binding domain of AgrA, which, in turn, triggers the induction of both the autoinducing peptide and RNAIII, ultimately causing the transcription of a series of toxin genes. The hypothesis is that blockage of the phosphohistidine pocket with a small molecule prevents toxin expression.