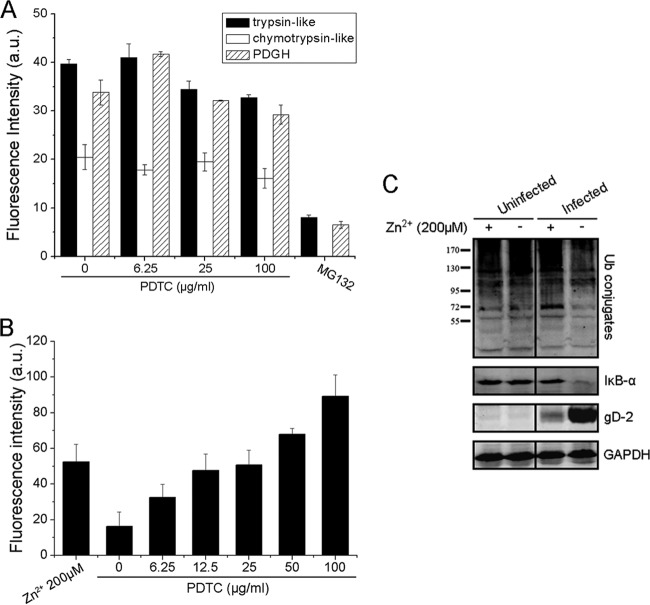
Fig 7.
The increased intracellular Zn2+ concentration mediated by PDTC might contribute to its inhibitory effect on 26S proteasome activity and its anti-HSV property. (A) PDTC did not inhibit 26S proteasome activity in a cell-free system. 26S proteasome activity was measured in the presence or absence of PDTC as described in the text. MG132 (2 μg/ml) was used as the positive control. (B) PDTC increased the intracellular Zn2+ level. Cells were incubated with PDTC or 200 μM Zn2+ for 30 min. The intracellular Zn2+ level was determined via FluoZin-3 AM labeling. (C) Zn2+ attenuated HSV-2-induced loss of ubiquitin conjugates and IκB-α and showed antiviral activity. HEC-1-A cells were either infected or not infected with HSV-2 (MOI = 1) in the presence or absence of Zn2+ (200 μM). Levels of ubiquitin conjugates, IκB-α, and gD were determined via Western blot assay 24 h p.i. Error bars show standard deviations.