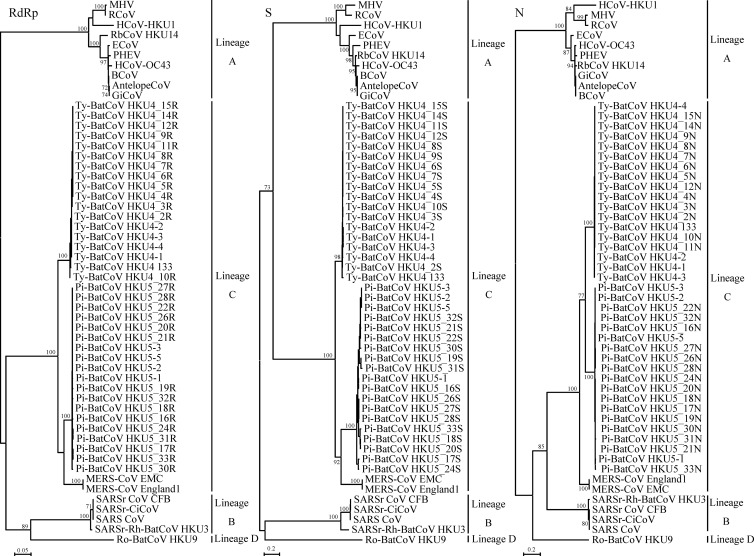
Fig 1.
Phylogenetic analysis of RdRp, S, and N genes of Ty-BatCoV HKU4 and Pi-BatCoV HKU5 strains and those of other betaCoVs with available complete genome sequences. The trees were constructed by the maximum-likelihood method with bootstrap values calculated from 100 trees. The analysis included 937, 1,535, and 546 aa positions in the RdRp, S, and N genes, respectively. The scale bars indicate the estimated number of substitutions per 5 or 20 aa. HCoV-HKU1, human coronavirus HKU1; HCoV-OC43, human coronavirus OC43; MHV, murine hepatitis virus; BCoV, bovine coronavirus; PHEV, porcine hemagglutinating encephalomyelitis virus; GiCoV, giraffe coronavirus; RCoV, rat coronavirus; ECoV, equine coronavirus; RbCoV HKU14, rabbit coronavirus HKU14; AntelopeCoV, sable antelope coronavirus; SARS-CoV, SARS coronavirus; SARSr-Rh-BatCoV HKU3, SARS-related Rhinolophus bat coronavirus HKU3; SARSr-CiCoV, SAR-related civet coronavirus; SARSr CoV CFB, SARS-related Chinese ferret badger coronavirus; Ty-BatCoV HKU4, Tylonycteris bat coronavirus HKU4; Pi-BatCoV HKU5, Pipistrellus bat coronavirus HKU5; MERS-CoV EMC, Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus EMC; MERS-CoV England1, Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus England1; Ro-BatCoV HKU9, Rousettus bat coronavirus HKU9.