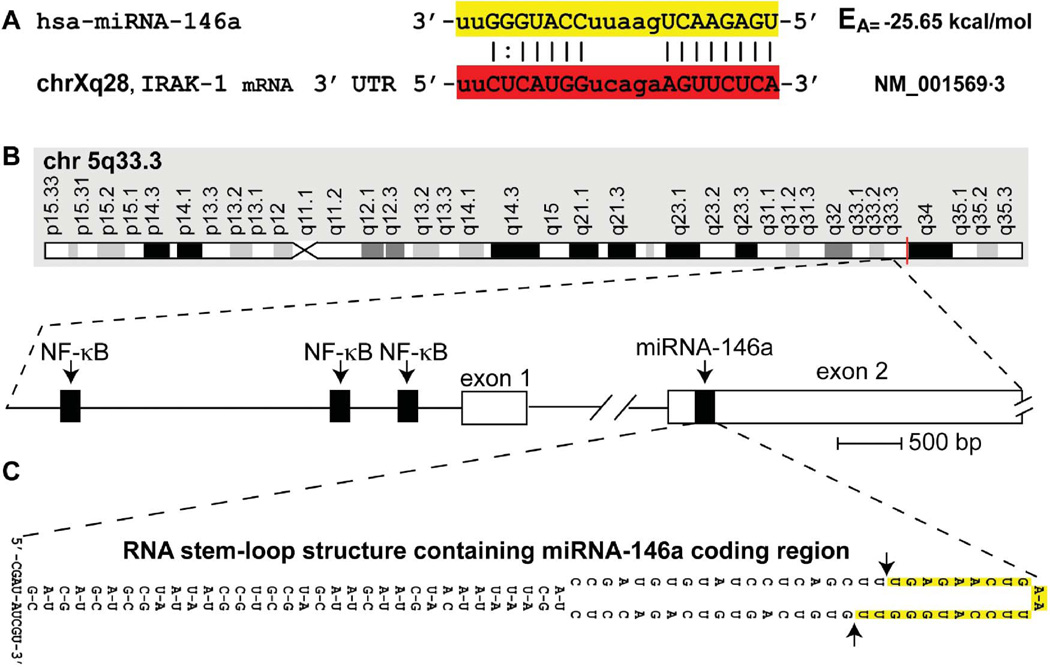
FIGURE 1.
(A) Homo sapiens micro RNA-146a (hsa-miRNA-146a) is a 22-nucleotide small RNA (highlighted in yellow) abundant in mouse and human immune cells and the limbic system, with known mRNA 3′ UTR targets that include the interleukin-1 receptor associated kinase 1 (IRAK-1; highlighted in red); uppercase ribonucleotides involved in fully (|) or partially (:) complementary hydrogen bonding (Cui et al. 2010; Taganov et al. 2006); chromosome location of the human IRAK-1 gene (chrXq28) and Genbank accession (NM_01569.3) indicated; EA = predicted energy of association for miRNA-mRNA interaction (Sethi and Lukiw 2009; miRBASE, Cambridge, UK); the mouse and human miRNA-146a are identical in sequence (Li et al. 2010a; 2010b; Sethi and Lukiw 2009). (B) Structural features of the miRNA-146a encoding DNA locus at chromosome 5q33.3 and details of the NF-κB-sensitive miRNA146a gene showing three upstream (5′) regulatory NF-КB binding sites; miRNA-146a transcription is highly NF-КB sensitive (Cui et al. 2010; Lukiw et al. 2008; Taganov et al. 2006). (C) The pre-miRNA-146a transcribed from the miRNA146a locus (chr 5q33.3) has strong potential to form a highly stable 35-base-pair stem, 60-nucleotide loop RNA structure (stem-loop EA= −49.5 kcal/mol); other predicted secondary structures of alternate stem-loop configurations are possible and the 5′ and 3′ ends of pre-miRNA-146a may be significantly extended. In several preferential EA models, such as the one depicted in (C), the stem-loop structure containing the miRNA-146a sequence is consistently located in the very distal end of the predicted loop (highlighted in yellow; delineated by arrows), after which Dicer (RNase III) processing of this pre-miRNA-146a (Yokota 2009) yields the mature miRNA-146a highlighted in yellow in (A) (color figure available online).