Figure 2.
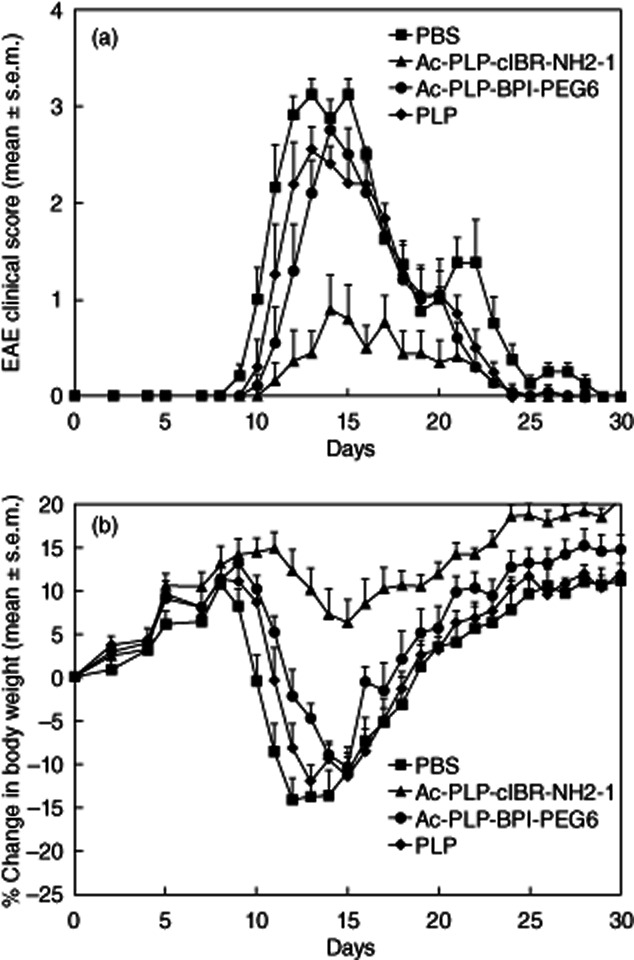
In-vivo experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE)-suppressive activity of Ac-PLP-cIBR-NH2-1 and control peptides in the EAE model to study the effects of a reduced dose and the importance of bifunctional peptide inhibitors (BPI) structure. proteolipid protein (PLP)139–151/complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA)-immunized mice received intravenous injections of vehicle or indicated peptides (50 nmol/injection/day on days 4 and 7). (a) Clinical EAE disease score. (b) Change in body weight. Results are expressed as the mean ± standard error of the mean (n = 10). Statistical values for EAE clinical scores and loss in body weight compared with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS)-treated mice were as follows: Ac-PLP-cIBR-NH2-1, P < 0·01; Ac-PLP-BPI-PEG6, P > 0·05; and PLP, P > 0·05.
