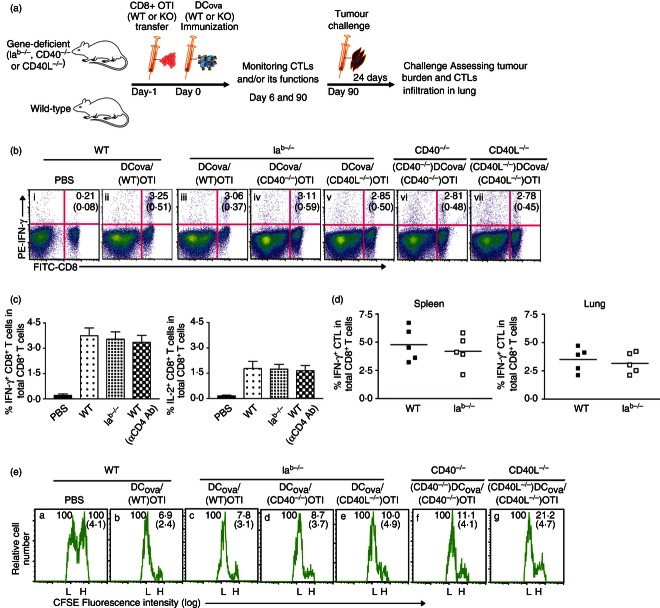
Figure 1.
Unhelped primary cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) generated from higher precursor frequency (PF) retain normal effector cytokine-secreting and cytotoxic functions. (a) A schematic protocol. Wild-type (WT) B6 or knockout mice were adoptively transferred with OTI CD8+ T cells [with or without CD40 or CD40 ligand (CDL molecules)] and intravenously immunized with ovalbumin (OVA) -pulsed dendritic cells (DCOVA) (with or without CD40 or CD40L). All the groups were monitored for CTL proliferation, survival and function during priming and memory stages. Ninety days later, all the groups were challenged with BL6-10OVA and assessed for protection. (b, c) After immunizing mice with higher PF, the blood samples were analysed by intracellular interferon-γ (IFN-γ; b, and c, left panel) or interleukin-2 (IL-2; c, right panel) staining assays 6 days later. The values in each figure or bar diagram represent mean % ± SD of IFN-γ+ or IL-2+ CTL in total CD8+ T-cell population, and are cumulative of two independent experiments with five or six mice per group. (d) The infiltration of IFN-γ+ CTLs was also determined in spleens and lungs of WT B6- and Iab−/−-immunized mice. The values represent frequencies of IFN-γ+ CTLs in the total CD8+ T-cell population, and are cumulative of two independent studies with two or three mice per group. The horizontal bars indicate means. (e) In the above immunized groups shown in (b), the proportions of CFSEhigh-OVAI-pulsed target cells lysed by effector CTL were determined in the spleen 7 days later by in vivo cytotoxicity assay. The values in each figure represent mean % ± SD of targets remaining in the spleen relative to the controls.