Table 3.
Factors influencing the efficiency of ORV programmes in the control and elimination of rabies. I, area index calculated until control, permanent control and elimination; P, proportion of territory ever affected; 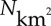 , number of detected cases per square kilometre at the start of ORV; events, the number of countries which achieved rabies control, permanent control or elimination during 1978–2010.
, number of detected cases per square kilometre at the start of ORV; events, the number of countries which achieved rabies control, permanent control or elimination during 1978–2010.
| Cox proportional hazard model | variable | transformation | hazard ratio (HR) | 95% CIs | significance (p) | n | events | pseudo R2 (max. possible)a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| control (90% reduction in rabies cases) | P | logit | 0.61 | 0.42–0.88 | 0.008 | 22 | 16 | 0.278 (0.943) |
| IC90 | logit | 1.439 | 0.97–2.13 | 0.069 | ||||
| permanent control (maintained 90% reduction) | 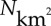 |
2.593 × 10−20 | 8.5 × 10−39−0.08 | 0.038 | 22 | 16 | 0.372 (0.943) | |
| P | logit | 0.588 | 0.40–0.86 | 0.007 | ||||
| IC90 | logit | 1.86 | 1.01–3.40 | 0.045 | ||||
| elimination | P | logit | 0.4541 | 0.27–0.76 | 0.003 | 22 | 11 | 0.411 (0.854) |
| IC100 | logit | 2.1679 | 1.11–4.23 | 0.023 |
aCox–Snell pseudo R2 value.
