Figure 4.
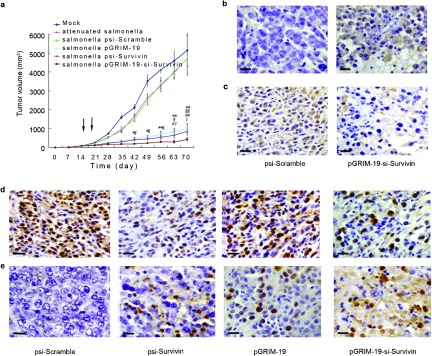
Intraperitoneal injection of attenuated Salmonella carrying different treatment plasmids resulted in significant inhibition of tumor growth and induction of apoptosis in prostate cancer grafts in vivo. (a) Growth curves of DU145 xenografts treated with attenuated Salmonella carrying recombinant plasmids (*P<0.05, **P<0.01 versus mock, §P<0.05, §§P<0.01 versus psi-Scramble group; #P<0.05, # # P<0.01versus psi-Survivin; ‖‖P<0.05, versus pGRIM-19 group). Arrows show Salmonella treatment carrying different plasmids through intraperitoneal at days 14 and 21. (b) Immunohistochemical analysis of Survivin expression for DU145 xenografts treated with S. typhimurium carrying psi-Scramble and pGRIM-19-si-Survivin plasmids. (c) Immunohistochemical analysis for GRIM-19 expression in DU145 xenografts treated with S. typhimurium carrying psi-Scramble and pGRIM-19-si-Survivin plasmids. (d) Immunohistochemical staining for Ki-67 in DU145 in vivo grafts; positive cells are brown. (e) TUNEL assay; TUNEL-positive cells are brown (scale bar=20 µm). GRIM-19, gene associated with retinoid-interferon-induced mortality-19; S. typhimurium, Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium; TUNEL, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated nick end labeling.
