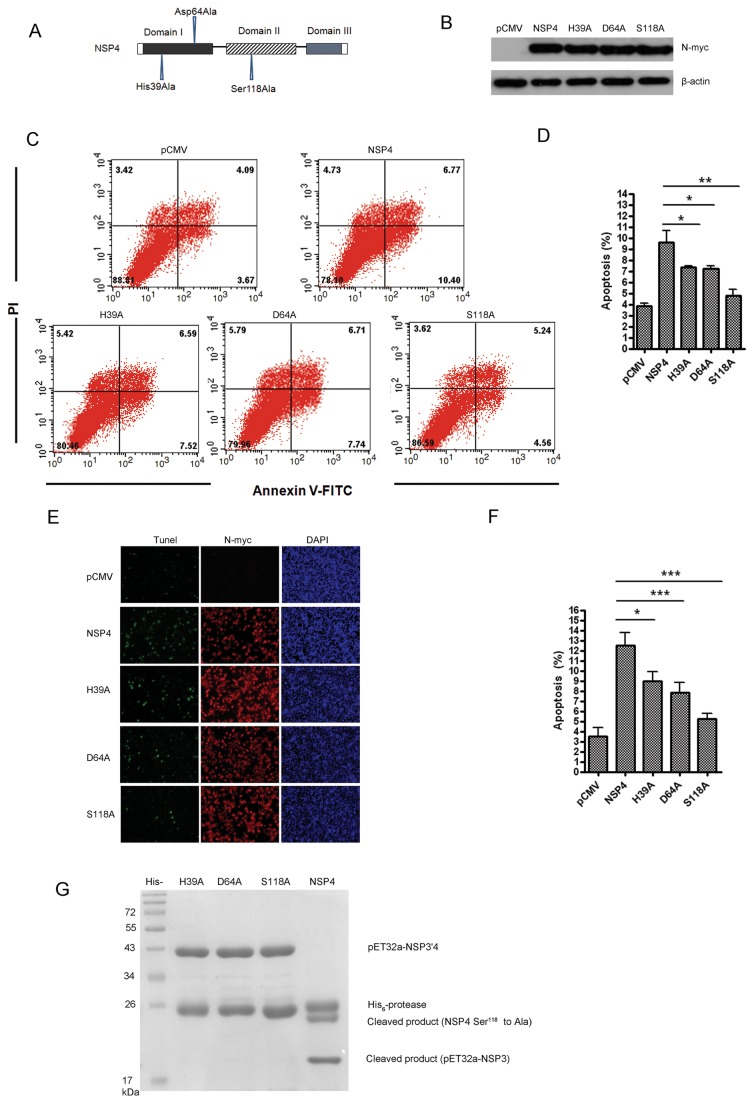
Figure 6. His39, Asp64, and Ser118 were required for nsp4 to induce apoptosis, and nsp4-induced apoptosis was dependent on its 3C-like serine protease activity.
(A) Schematic diagram of the PRRSV nsp4 protein and point mutant constructs. (B) Expression of nsp4, H39A, D64A, and S118A point mutant proteins in Hela cells. Cells were transfected with wild-type nsp4, H39A, D64A, or S118A point mutant plasmid. At 48 hours post transfection, cell lysates were prepared and examined with western blotting. (C) Flow cytometry analysis of nsp4, H39A, D64A, or S118A-induced apoptosis in Hela cells at 48 hours post transfection. (D) Percentage of apoptotic cells in panel C. Data are representatives of three independent experiments. (E) Double-labeling immunofluorescence analysis using TUNEL for apoptosis and indirect immunofluorescence for wild-type and the point mutant nsp4 proteins in Hela cells at 48 hours post transfection. Apoptosis (green), wild-type or mutant nsp4 (red), and nucleus (blue) were detected. (F) Percentage of apoptotic cells in panel E. (G) Proteolytic reaction was mediated by PRRSV wild-type and point mutant nsp4 proteins. The wild-type or point mutant nsp4 proteins were incubated with the substrate NSP3’ 4 (Ser118Ala) for 24 h. Lanes 2 through 5, H39A, D64A, S118A, and wild-type nsp4. Graphs show means ± SD from three independent experiments. P<0.05 (*), P<0.01 (**), P<0.001 (***) as determined by student’s t test.