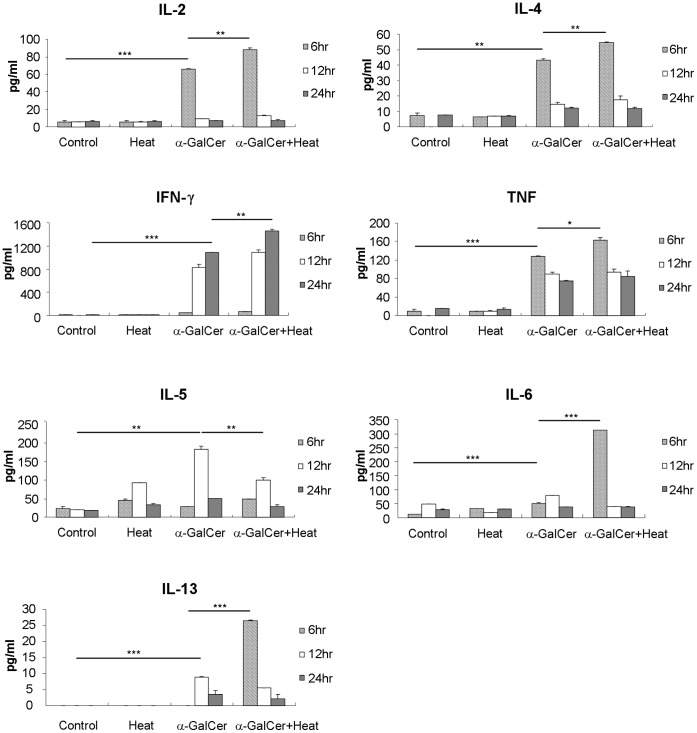
Figure 1. Th1/Th2 cytokine expression in serum of i.p. hyperthermia and/or α-GalCer treated mice.
C57BL/6 mice were divided into 4 groups with 5 mice for each group and treated with i.p. hyperthermia only at 43°C for 10 min, i.p. added 2 µg of α-GalCer, and combining both. The control group mice were only performed exploratory laparotomy for 10 min. Mouse serum was collected at 6, 12, and 24 hr after treatment. IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, Interferon-γ, TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-13 concentrations of serum were detected by multiplex CBA kit. Some cytokine levels were increased by α-GalCer and peaked at 6 hr post-treatment (IL-2, p = 0.0003, α-GalCer alone versus control), (IL-4, p = 0.0012, α-GalCer alone versus control), (IL-6, p<0.0001, α-GalCer versus control), (TNF-α, p = 0.0007, α-GalCer versus control); Some peaked at 12 hr after treatment (IL-5, p = 0.0013, α-GalCer versus control) (IL-13, p<0.0001, α-GalCer versus control); one peaked at 24 hr after treatment (INF-γ, p<0.0001, α-GalCer versus control). Except for IL-5, the Th1/Th2 cytokine levels were higher in combined treatment group than α-GalCer alone group (IL-2, p = 0.0056; IL-4, p = 0.0041; TNF-α, p = 0.018; INF-γ, p = 0.0058). The peak level of IL-13 was reached earlier in the combined treatment group and its level was much higher than that of α-GalCer alone (p<0.0001). These results implied that α-GalCer treatment could trigger immune response toward Th1/Th2 route and hyperthermia could further enhance this effect. (# p<0.05; * p<0.01; ** p<0.001; *** p<0.0001).