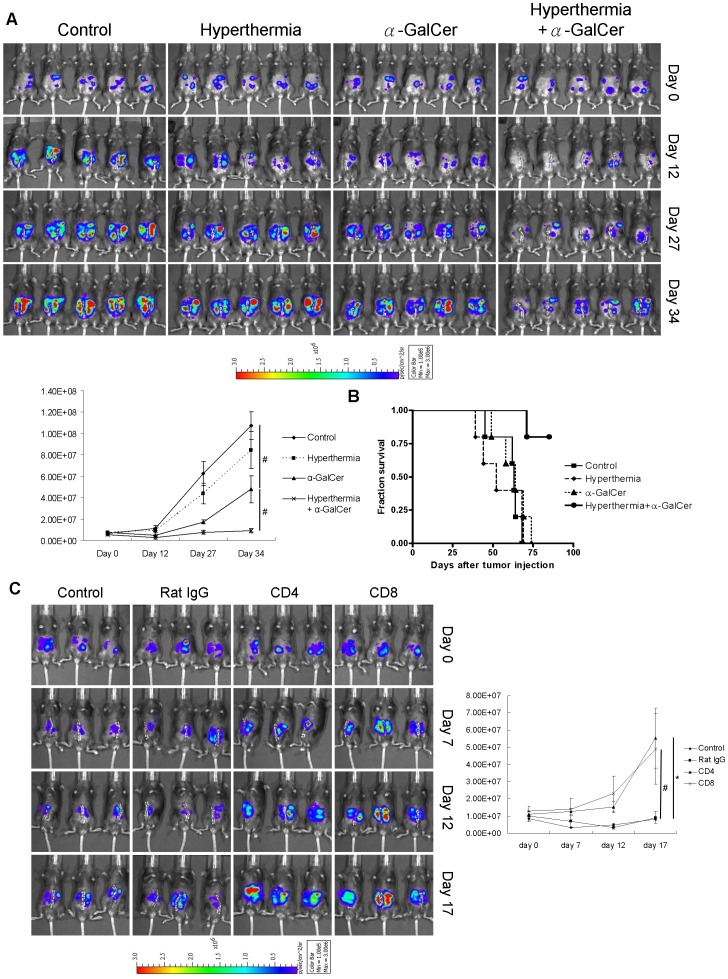
Figure 5. Intra-peritoneal hyperthermia enhanced the anti-tumor effect of α-GalCer in mouse ovarian cancer model.
(A) One million of MOSEC-luc cells were i.p. injected into C57BL/6 mice. Seven days later, the mice were divided into 4 groups and treated as described previously. Tumor growth was recorded and represented by the intensities of chemo-luminescence detected by IVIS imaging system. The results showed that α-GalCer could inhibit the tumor growth and the combined treatment exerted even stronger inhibition. (B) Survival curve on each group revealed that there is no significant difference in survival of control, hyperthermia alone and α-GalCer treated groups. However, combinational treatment could clearly extend the survival of the treated mice. (C) One million of MOSEC-luc cells were i.p. injected into C57BL/6 mice. Seven days later, the mice were divided into 4 groups and received i.p. injection of either 100 µg of rat IgG, rat anti-mouse CD4 or rat anti-mouse CD8 neutralizing antibody every 2 days. Mice without injection of neutralizing antibodies were set as control group. Intra-peritoneal hyperthermia plus α-GalCer treatment was given to all mice on day 7. Tumor growth was recorded and represented by the intensity of chemo-luminescence detected by non-invasive IVIS imaging system. The results showed that administration of mouse CD4 and CD8 neutralizing antibodies abrogated the anti-tumor effect, which implied both CD4+ and CD8+ T cell contribute to the anti-tumor effect. (# p<0.05; *p<0.01).