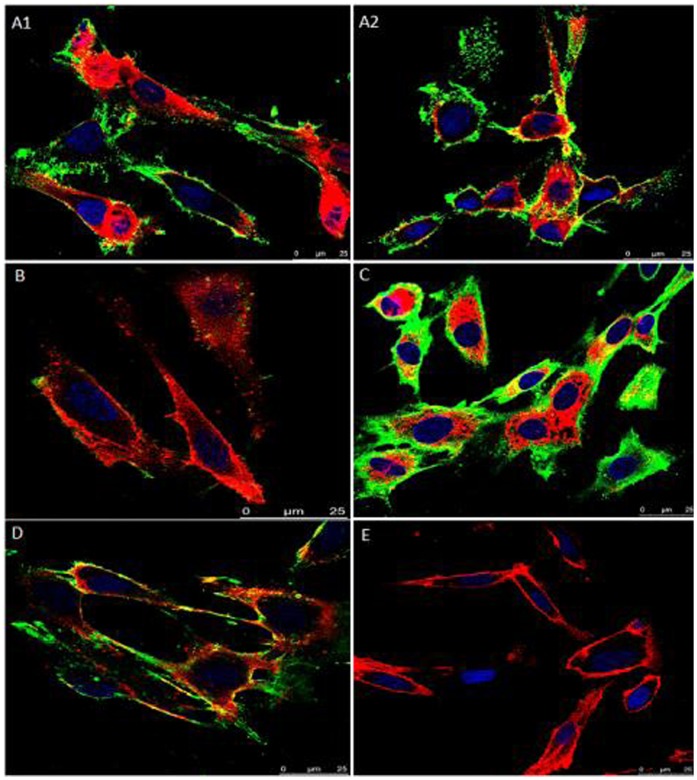
Figure 2. Assay of rVpmaX adhesion and adhesion inhibition to EBL cells visualized by confocal laser scanning microscopy.
Active rVpmaX interacted with fixed EBL cells, and the surplus protein was rinsed away by washing with PBST. The attached protein was immunostained with rabbit anti-rVpmaX antibody and mouse anti-rabbit IgG-FITC. The EBL cell membranes were labeled with 1,19-dioctadecyl-3,3,3′,3′-tetramethylindocarbocyanine perchlorate (DiI), and the cell nuclei were counter-labeled with 49,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). (A1–A2) 10 µg rVpmaX adhering to EBL cells. (B) Adhesion inhibition of 10 µg rVpmaX to EBL cells by 10 µl rabbit anti-rVpmaX serum. (C) Adhesion of 20 µg rVpmaX to EBL cells. (D) The adhesion of 20 µg rVpmaX to EBL cells was inhibited by 20 µl rabbit anti-rVpmaX serum. (E) EBL cells without protein added.