Figure 5.
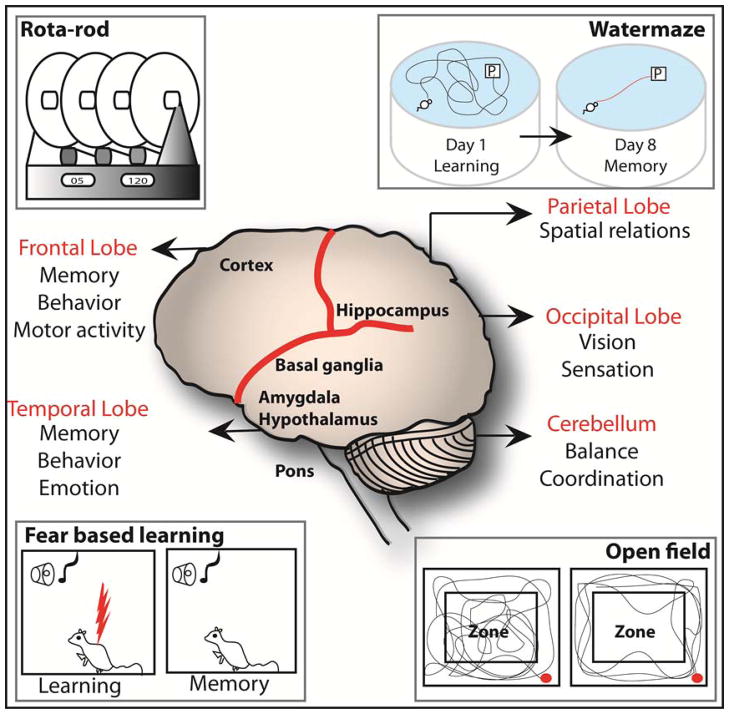
Brain components and related behavior tests: Figure 4. Various brain regions and functions are highlighted. Behavioral tests that test specific brain regions are shown. The hippocampus in the parietal lobe is important for learning spatial relationships and can be studied using a water maze. The amygdala mainly creates emotions including fear that can be measured using fear-conditioning test. Fear based learning utilizes freezing time as a measure of change in behavior to a repeated and alternative aversive and neutral stimuli given to the animal on the training day. Open field test is used to measure anxiety and general locomotion and these actions are controlled by amygdala and cerebellum. The rota-rod machine measures the motor function including balance and coordination of movement. Control of motor function is performed by the combine action of the cerebellum, basal ganglia and cortex in the frontal lobe.