Figure 4. GPI-specific B cells remain naïve in Msr1−/− K/BxN mice.
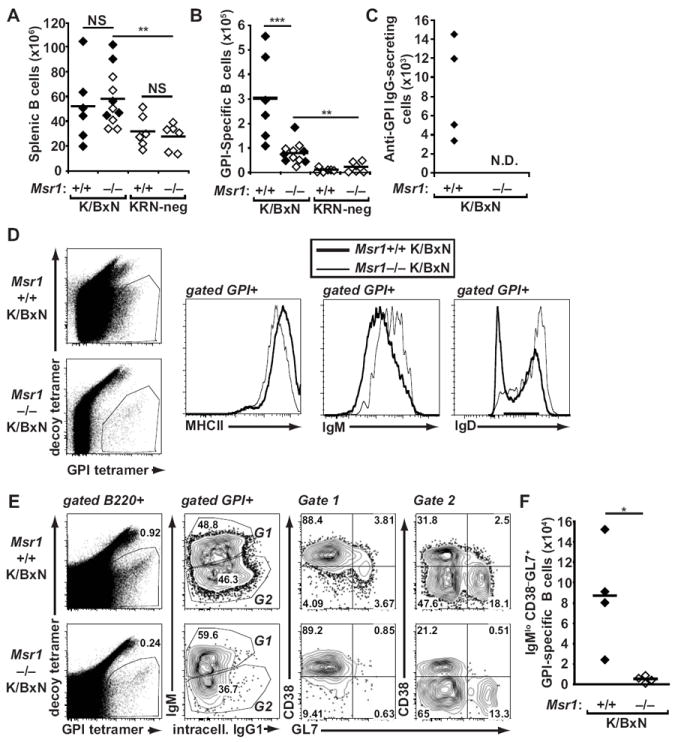
(A) Splenic B220+ B cells and (B) GPI-specific B cells from spleen and lymph nodes of 8-week-old Msr1+/+ and Msr1−/− K/BxN mice, as well as KRN-negative Msr1+/+ and Msr1−/− mice were analyzed by flow cytometry using antigen-specific and antigen-nonspecific B cell tetramers. Each point represents one animal; filled diamonds indicate arthritic animals, open diamonds indicate non-arthritic animals, and bars represent means; data were compiled from three independent experiments; **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001. (C) The number of anti-GPI IgG-secreting cells was determined by ELISPOT in mice of the indicated genotypes. Data are representative of two independent experiments. In Msr1−/− K/BxN mice, these numbers were below the limit of detection for the assay (N.D. = not detected). (D) GPI-specific B cells from spleens and lymph nodes of mice of the indicated genotypes were assessed for cell surface expression of MHCII, IgM, and IgD. (E) Expression of surface IgM and intracellular IgG1 and CD38 and GL7 among GPI-specific lymph node and splenic B cells was determined in mice of the indicated genotypes. Naïve B cells are IgMhiCD38+GL7−, whereas germinal center B cells are IgMloCD38−GL7+ For D and E, the numbers indicate the percentage of cells in each quadrant or gate; results are representative of experiments performed with 3-4 mice/genotype. (F) The absolute number of GPI-specific IgMlo CD38−GL7+ germinal center B cells is depicted for the two groups of mice. Data represent two experiments with 4 mice/genotype; * p<0.05.
