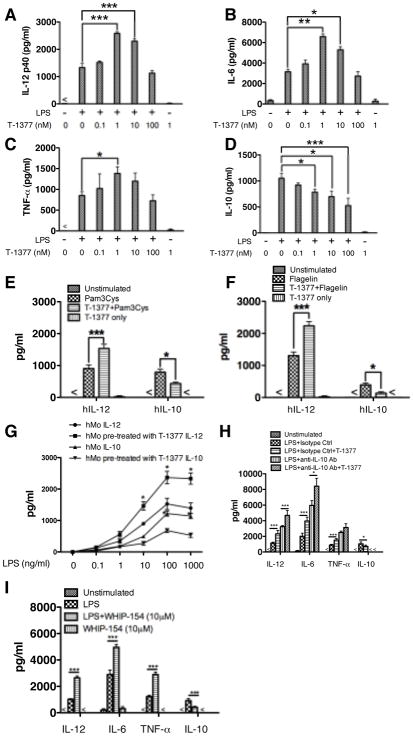
Figure 1. JAK3 inhibitors differentially regulate TLR4-mediated inflammatory cytokine production in human monocytes.
Purified human monocytes were pre-treated with different JAK3 inhibitors (T-1377 or WHIP-154 (10μM)) or IL-10 neutralizing antibody (5 μg/ml) using rat IgG1 as an isotype control for 2 hours, and then stimulated with LPS (1μg/ml), Pam3CSK4 (500 ng/ml), or Flagelin (5 μg/ml). After 24 h of stimulation, the cell-free supernatants were collected and the levels of (A) IL-12p40, (B) IL-6, (C) TNF-α, and (D) IL-10 were determined by ELISA. For A–D, lower concentration of T-1377 (<10 nM) enhanced the production of IL-12p40 (A), IL-6 (B), and TNF- α (C) while suppressing IL-10 levels (D) produced by LPS-stimulated human monocytes. JAK3 inhibition by 1 nM T-1377 also differentially regulated production of IL-12 and IL-10 in TLR2- or TLR5-stimulated monocytes (E, F). With different doses of LPS, 1 nM T-1377 exhibited a similar regulatory effect on the production of IL-12 and IL-10 (G). In the context of IL-10 neutralization, JAK3 inhibition (1n M T-1377) remains capable of enhancing LPS-mediated pro-inflammatory cytokine production (H). A second JAK3 inhibitor WHIP-154 (10 μM) showed the same capability to increase or decrease the production of IL-12p40, IL-6, TNF-α and IL-10 (I), respectively. *, **, and *** indicates statistically significant at P<0.05, P<0.01, and P<0.001, respectively. Data represents the arithmetic mean ± S.D. of three biological replicates.