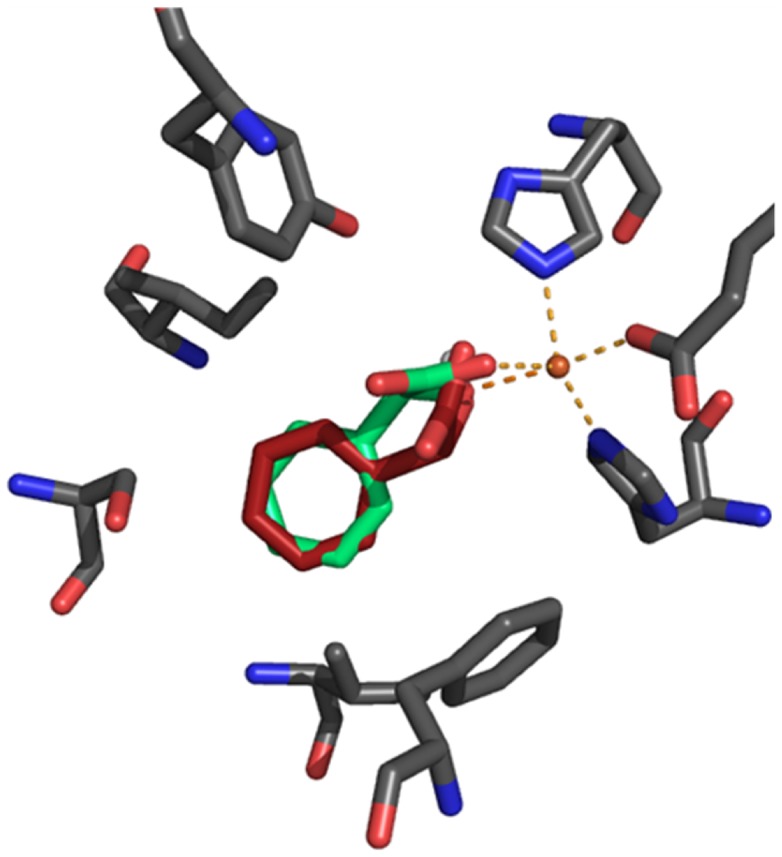
Figure 5. Overlay of (R)-mandelate and (S)-mandelate ligands docked into the S. coelicolor Hms model in silico.
The (S)-mandelate (green) coordinated structure showed a slightly distorted trigonal bipyramidal geometry that mirrors crystal structural data of the A. orientalis HMS product complex (PDB: 2R5V) with angle deviations <2°. In the (R)-mandelate (red) bound model, the positions of the axial ligands, namely the carboxylate oxygen from Glu340 and the hydroxy oxygen from mandelate, were preserved. However, the residues that form the trigonal plane showed major deviations from ‘ideal’ geometry: Angles between the coordinated (R)-mandelate’s carboxylate oxygen, the iron cofactor and the histidines’ metal-nitrogens shifted from 110° to 139° (His 181) and from 124° to 100° (His261), respectively.